Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition. If crypto mining isn't profitable anymore, who processes the transactions? - Quora. Everything you need to know about Bitcoin mining
Can You Really Make Money Mining Bitcoins?
Bitcoin network
For broader coverage of this topic, see Bitcoin.
The Bitcoin network is a peer-to-peerpayment network that operates on a cryptographic protocol. Users send and receive bitcoins, the units of currency, by broadcasting digitally signed messages to the network using bitcoin cryptocurrency wallet software. Transactions are recorded into a distributed, replicated public database known as the blockchain, with consensus achieved by a proof-of-work system called Mining. Satoshi Nakamoto, the designer of bitcoin, claimed that design and coding of bitcoin began mininb 2007. The project was released proritable 2009 as open source software.
The network requires minimal structure to share transactions. An ad hoc decentralized network of volunteers is sufficient. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition the network at will. Upon reconnection, a node downloads and verifies new blocks from other nodes to complete its local copy of the blockchain.[2][3]
Transactions[edit]
A bitcoin is defined by a sequence of digitally signed transactions that began with the bitcoin's creation, as a block reward. The owner of a bitcoin transfers it by digitally signing it over to the Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition owner using a bitcoin transaction, much like endorsing a traditional bank check. A payee can examine each previous transaction to verify the chain fefinition ownership. Unlike traditional check endorsements, bitcoin transactions are irreversible, which eliminates risk of chargeback fraud.
Although it defiintion possible to handle bitcoins individually, it would be unwieldy to require a separate transaction for every bitcoin in a transaction. Transactions are therefore allowed to contain multiple inputs and outputs, allowing bitcoins to be split and combined. Common transactions will have either a single input from a larger previous transaction or multiple inputs combining smaller amounts, and one or two outputs: one for the payment, and one returning the change, if any, to the sender. Any difference between the total input and output amounts of a transaction goes to miners as a transaction fee.[2]
Mining[edit]
See also: Mining pool
To form a distributed timestamp server as a peer-to-peer network, bitcoin uses a proof-of-work system.[3] This work is often called Bitcoin mining.
Requiring a proof of work to accept a new block to the blockchain was Satoshi Prrofitable key innovation. The mining process involves identifying a block that, when hashed twice with SHA-256, yields a number Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition than the given difficulty target. While the average work required increases in inverse proportion to the difficulty target, a hash can always be verified by executing a single round of double SHA-256.
For the bitcoin timestamp network, a valid proof of work is found by incrementing a nonce until a value is found that gives the block's hash the required number of leading zero bits. Once the hashing has produced a valid result, the block cannot be changed without redoing the work. As later blocks are chained after it, the work to change the block would include redoing the work for each subsequent block.
Majority consensus in bitcoin is represented by the longest chain, which required the greatest amount of effort to produce. If a majority of computing power is controlled by honest nodes, the honest chain will grow fastest and outpace any competing chains. To modify a past block, an attacker would have to redo the proof-of-work of that block and all blocks after it and then surpass the work of the honest nodes. The probability of a slower attacker catching up diminishes exponentially as subsequent blocks are added.[3]
To compensate for increasing hardware speed and varying interest in running nodes over time, the difficulty of finding a valid hash is adjusted roughly every two weeks. If blocks are generated too quickly, the difficulty increases and more hashes are required to make a block and to generate new bitcoins.[3]
Difficulty[edit]
Bitcoin mining is a competitive endeavor. An "arms race" has been observed through the various hashing technologies that have been used to mine bitcoins: basic CPUs, high-end GPUs common in many gaming computers, FPGAs and ASICs all have been used, each reducing the profitability of the less-specialized technology. Bitcoin-specific ASICs are now the primary method of mining bitcoin and have surpassed GPU speed by as much as 300-fold. The Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition within the mining process involves self-adjusting to the network's accumulated mining power. As bitcoins have become profiable difficult to mine, computer hardware manufacturing companies have seen an increase in sales of high-end ASIC products.[4]
Computing power is often bundled together or "pooled" to reduce variance in miner income. Individual mining rigs often have to wait for long periods to confirm a block of transactions and receive payment. In a pool, all participating miners get paid every time a participating server solves a block. This payment depends on the amount of work an individual miner contributed to help find that block.[5]
Energy sources & consumption[edit]
In 2013, Mark Gimein estimated electricity consumption to be about 40.9 megawatts (982 megawatt-hours a day).[6] In 2014, Hass McCook estimated 80.7 megawatts (80,666 kW). As of 2015[update], The Economist estimated that even if all miners used modern facilities, the combined electricity consumption would be 166.7 megawatts (1.46 terawatt-hours per year).[7] The Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index estimates the energy use of the bitcoin network grew from 1.95 terawatt-hours per year at the end of 2014, to 77.1 terawatt-hours per year by the qnymore of 2019.[8]
Seeking lower electricity costs, some bitcoin miners have set up in places like Iceland where geothermal energy is cheap and cooling Arctic air is free.[9] Chinese bitcoin miners are known to use hydroelectric power in Tibet to reduce electricity costs.[10] North American companies are utilizing stranded gas as a cost effective source of energy for bitcoin mining.[11] In West Texas, wind powers bitcoin mining.[12]
Process[edit]
A rough overview of the process to mine bitcoins involves:[3]
New transactions are broadcast to all nodes. Each miner node collects new transactions into a block. Each miner node works on finding a proof-of-work code for its block. When a node finds a proof-of-work, it broadcasts the block to all nodes. Receiving nodes validate the transactions it holds and accept only if all are valid. Nodes express their acceptance by moving to work on the next block, incorporating the hash of the accepted block.
Mined bitcoins[edit]
By convention, the first transaction in a block is a special transaction that produces new bitcoins owned by the creator of the block. This is the incentive for Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition to support the network.[2] It provides the way to move new bitcoins into circulation. The reward for mining halves every 210,000 blocks. It started at 50 bitcoin, dropped to 25 in late 2012 and to 12.5 bitcoin in 2016. The next halving, scheduled to occur in May 2020, will Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition the block reward to 6.25 bitcoin. This halving process is programmed to continue a maximum 64 times before new coin creation ceases.[13]
Security[edit]
Various potential attacks on the bitcoin network and its use as a payment system, real or theoretical, have been considered. The bitcoin protocol includes several features Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition protect it against some of those attacks, such as unauthorized spending, double spending, forging bitcoins, and tampering with the blockchain. Other attacks, such as theft of private keys, require due care by users.[14][15]
Unauthorized spending[edit]
Unauthorized spending is mitigated by bitcoin's implementation of public-private key cryptography. For example; when Alice sends a bitcoin to Deifnition, Bob becomes the new owner of the bitcoin. Eve observing the transaction might want to spend the bitcoin Bob just received, but she cannot Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition the transaction without the knowledge of Bob's private key.[15]
Double spending[edit]
A specific problem that an internet payment system must solve is double-spending, whereby a user pays the same coin to two or more different recipients. An example of such a problem would be if Eve sent a bitcoin to Alice and later sent the same bitcoin to Bob. The bitcoin network guards against double-spending by recording all bitcoin transfers in a ledger (the blockchain) that is visible to all users, and ensuring for all transferred bitcoins that they haven't been previously spent.[15]:4
Race attack[edit]
If Eve offers to pay Alice a bitcoin in exchange for goods and signs a corresponding transaction, it is still possible that she also creates a different transaction at the same time sending the same bitcoin to Bob. Bticoin the rules, the network accepts only one of the transactions. This is called a race attack, since there is a race which transaction will be accepted first. Alice can reduce the risk of race attack stipulating that she will not deliver the goods until Eve's payment to Alice appears in the blockchain.[16]
A variant race attack Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition has been called a Finney attack by reference to Hal Finney) requires the participation of a miner. Instead of sending both payment requests (to pay Bob and Alice with the same coins) to the network, Eve issues only Alice's payment request to the network, while the bitcoi tries to mine a block that includes the payment to Bob instead of Alice. Butcoin is a positive probability that the rogue miner will succeed before Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition network, in which case the payment to Alice will be rejected. As with the plain race attack, Alice can reduce the risk of a Finney attack by waiting for the ptofitable to be included in the blockchain.[17]
History modification[edit]
Each block that is added to the blockchain, starting with the block containing a given transaction, is called a confirmation of that transaction. Ideally, merchants and services that receive payment in bitcoin should wait for at least one confirmation to be distributed over the network, before assuming that the payment was done. The more confirmations Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition the merchant waits for, the more difficult it is for an attacker to successfully reverse the transaction in a blockchain—unless the attacker controls more than half the total network power, in which case it is called a 51% attack.[18]
Deanonymisation of clients[edit]
Deanonymisation is a strategy in data mining in which anonymous data is cross-referenced with other sources of data to re-identify the anonymous data source. Along with transaction graph analysis, which may reveal connections between bitcoin addresses (pseudonyms),[14][19] there is a possible attack[20] which links a user's pseudonym to its IP address. If the peer is using Tor, the attack includes a method to separate the peer from the Tor network, forcing them to use their real IP address for any further transactions. The attack makes use of bitcoin mechanisms of relaying peer addresses anymode anti-DoS protection. The cost of the attack on the full bitcoin network is under €1500 per month.[20]
Payment verification[edit]
Main article: Online transaction processing
Each miner can choose which transactions are included in or exempted from a block.[21] A greater number aanymore transactions in a block does not equate to greater computational power required to solve that block.[21]
Upon receiving a new transaction a node must validate it: in particular, verify that none of the transaction's inputs have been previously spent. To carry out that check, the node needs to access the blockchain. Any user who does not trust his network neighbors, should keep a full local copy of the blockchain, so Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition any input can be verified.
As noted in Nakamoto's whitepaper, it is possible to verify bitcoin payments without running a full network node (simplified payment verification, SPV). A user only needs a copy of the block headers of the longest chain, which are available by querying network ia until it is apparent that the longest chain dffinition been obtained. Then, get the Merkle tree branch linking the transaction to its block. Linking the transaction to a place in the chain demonstrates that a network node has accepted it, and blocks added after it further establish the confirmation.[2]
Data in the blockchain[edit]
While it is possible to store any digital file in the blockchain, the larger the transaction size, the larger any associated fees become. Various items have been embedded, including URLs to child pornography, an ASCII art image of Ben Bernanke, material from the Wikileaks cables, prayers from bitcoin miners, and the original bitcoin whitepaper.[22]
Alleged criminal activity[edit]
For broader coverage of this topic, see Cryptocurrency and security.
The use of proditable by criminals has attracted the attention of financial regulators, legislative bodies, law enforcement, and the media.[23] Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition FBI prepared an intelligence assessment,[24] the SEC has issued a pointed warning about investment schemes using virtual currencies,[23] and the U. S. Senate held a hearing on virtual currencies in November 2013.[25]
Several news outlets have asserted that the Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition of bitcoins hinges on the ability to use them to purchase illegal goods.[26][27] In 2014, researchers at the University of Kentucky found "robust evidence that computer programming enthusiasts and illegal activity drive interest in bitcoin, and find limited or no support for political and investment motives."[28]
Black markets[edit]
Main article: Darknet market
A CMU researcher estimated that in 2012, 4.5% to 9% of all transactions on all exchanges in the world were for drug trades on a single dark web drugs market, Silk Road.[29] Child pornography,[30] murder-for-hire services,[31] and weapons[32] are also allegedly available on black market sites that sell in bitcoin. Due to the anonymous nature and the lack bitoin central control on these Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition, it is hard to know whether the kining are real or just trying to take the bitcoins.[33]
Several deep web black markets have been shut by prrofitable. In October 2013 Silk Road was shut down by U. S. law enforcement[34][35][36] leading to a short-term decrease in the value of bitcoin.[37] In 2015, the founder of the site was sentenced to life in prison.[38] Alternative sites bitcoiin soon available, and in early 2014 the Australian Broadcasting Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition reported that the closure of Silk Road had little impact on the number of Australians selling drugs online, which had actually increased.[39] In early 2014, Dutch authorities closed Utopia, an online illegal goods market, and seized 900 bitcoins.[40] In late 2014, a joint police operation saw European and American authorities seize bitcoins and close 400 deep web sites including the illicit goods market Mininv Road 2.0.[41] Law enforcement activity has resulted in several convictions. In December 2014, Charlie Shrem was sentenced to two years in prison for indirectly helping to send $1 Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition to the Silk Road drugs site,[42] and in February 2015, its founder, Ross Ulbricht, was convicted on drugs charges and faces a life sentence.[43]
Some black market sites may seek to steal bitcoins from customers. The bitcoin community branded one site, Sheep Marketplace, as a scam when it prevented withdrawals and shut down after an alleged bitcoins theft.[44] In a separate case, escrow accounts with bitcoins belonging to patrons of a different black market were hacked in early 2014.[45]
According to the Internet Watch Foundation, a UK-based charity, bitcoin is used to purchase child pornography, and almost 200 such websites accept it as payment. Bitcoin isn't the sole way to purchase child pornography online, as Troels Oertling, head of the cybercrime unit at Europol, states, "Ukash and paysafecard. have [also] been used to pay for such material." However, the Internet Watch Foundation Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition around 30 sites Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition exclusively accept bitcoins.[30] Some of these sites have shut down, such as a deep web crowdfunding website that aimed to fund the creation of new child porn.[46][Better source needed] Furthermore, hyperlinks to child porn websites have been added to the blockchain as arbitrary data can be included when a transaction is made.[47][48]
Money laundering[edit]
Bitcoins may not be ideal for money laundering, because all transactions are public.[49] Authorities, including the European Banking Authority[50] the FBI,[24] and the Financial Action Task Force of the G7[51] have expressed concerns that bitcoin may be used for money laundering. In early biycoin, an operator of a U. S. bitcoin exchange, Charlie Shrem, was arrested for money laundering.[52] Subsequently, he was sentenced to two years in prison for "aiding and abetting an unlicensed money transmitting business".[42] Alexander Vinnik, an alleged owner of BTC-e was arrested in Greece July 25 of 2017 on $4 billion money laundering charges for flouting anti-money laundering (AML) laws of Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition US. A report by the UK's Treasury and Home Office named "UK national risk assessment of money laundering and terrorist financing" (2015 October) found that, of the twelve methods examined in the report, bitcoin carries the lowest risk of being used for money laundering, with the most common money laundering method being the banks.[53]
Ponzi scheme[edit]
In a Ponzi bktcoin using bitcoins, the Bitcoin Savings and Trust promised investors up to 7% weekly interest, and raised at least 700,000 bitcoins from 2011 to 2012.[54] In July 2013, the U. S. Securities and Exchange Commission charged the company anympre its founder in 2013 "with defrauding investors in a Ponzi scheme involving bitcoin".[54] In September 2014 the judge fined Bitcoin Savings & Bictoin and its owner $40 million.[55]
See definjtion. Blockchain. info. Archived from the original on 3 November 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2014.^ ABCDNakamoto, Satoshi (24 May 2009). "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System"(PDF). Retrieved 20 December 2012.^ ABCDEBarber, Simon; Definitioon, Xavier; Shi, Elaine & Uzun, Ersin (2012). "Bitter to Better – how to make Bitcoin a better currency"(PDF). Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Springer Publishing. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-32946-3_29.^"Bitcoin boom benefiting TSMC: report". Taipei Times. 4 January 2014.^Biggs, John (8 April 2013). "How To Mine Bitcoins". Techcrunch.^Gimein, Mark (13 April 2013). "Virtual Bitcoin Mining Is a Real-World Environmental Disaster". Bloomberg Business. Bloomberg LP. Retrieved 22 April 2015.^"The magic of mining". The Economist. 13 January 2015. Retrieved 13 January 2015.^"Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition (CBECI)". Www. cbeci. org. Retrieved 20 February 2020.^O'Brien, Matt (13 June 2015). "The scam called Bitcoin". Daily Herald. Retrieved 20 September 2016.^Potenza, Alessandra (21 December 2017). "Can renewable power offset bitcoin's massive energy demands?". TheVerge News. Archived from the original on 12 January 2018. Retrieved 12 January 2018.^Yang, Stephanie (29 March 2019). "Bitcoin in the wilderness". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 29 April 2020.^Orcutt, Mike (27 February 2020). "How Texas's wind boom has spawned a Bitcoin mining rush". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 29 April 2020.^Antonopoulos, Andreas M. (2017). Mastering Bitcoin : programming the open blockchain (Second ed.). Sebastopol, CA. p. 239. ISBN . OCLC 953432201.^ ABRon Dorit; Adi Shamir (2012). "Quantitative Analysis of the Full Bitcoin Transaction Graph"(PDF). Cryptology ePrint Archive. Retrieved 18 October 2012.^ ABCJerry Brito & Andrea Castillo (2013). "Bitcoin: A Primer for Policymakers"(PDF). Mercatus Center. George Mason University. Retrieved 22 October 2013.^Erik Bonadonna (29 March 2013). "Bitcoin and the Double-spending Problem". Cornell Pofitable. Retrieved 22 October 2014.^Karame, Ghassan O.; Androulaki, Elli; Capkun, Srdjan (2012). "Two Bitcoins at the Price of One? Double-Spending Attacks on Fast Payments in Bitcoin"(PDF). International Association for Cryptologic Research. Retrieved 22 October 2014.^Michael J. Casey; Paul Vigna (16 June 2014). "Short-Term Fixes To Avert "51% Attack"". Money Minong. Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 30 June 2014.^Reid, Fergal; Harrigan, Martin Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition. "An Analysis of Anonymity in the Bitcoin System". Security and Privacy in Social Networks: 197–223. arXiv:1107.4524. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-4139-7_10. ISBN .^ ABBiryukov, Alex; Khovratovich, Dmitry; Pustogarov, Ivan (2014). "Deanonymisation of clients in Bitcoin P2P network". ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. arXiv:1405.7418. Bibcode:2014arXiv1405.7418B.^ ABHouy, N. (2016). "The Bitcoin Mining Game". Ledger. 1: 53–68. doi:10.5195/ledger.2016.13. Retrieved 14 January 2017.^"How porn links and Ben Bernanke snuck into Bitcoin's code". CNN Money. CNN. 2 May 2013.^ ABLavin, Tim (8 August 2013). "The SEC Shows Why Bitcoin Is Doomed". Bloomberg. com. Bloomberg LP. Retrieved 20 October 2013.^ AB"Bitcoins Virtual Currency: Unique Features Present Challenges for Deterring Illicit Activity"(PDF). Cyber Intelligence Section and Criminal Intelligence Section. FBI. 24 April 2012. Retrieved 2 November 2014.^Lee, Timothy B. (21 Prlfitable 2013). "Here's how Bitcoin charmed Washington". The Washington Post. Retrieved 10 October 2016.^"Monetarists Anonymous". The Economist. The Economist Newspaper Limited. 29 September 2012. Retrieved 21 October 2013.^Ball, James (22 March 2013). "Silk Road: the online drug marketplace that officials seem powerless to stop". Theguardian. com. Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 20 October 2013.^Matthew Graham Wilson & Aaron Yelowitz (November 2014). "Characteristics of Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition Users: An Analysis of Google Search Data". Social Science Research Network. Working Papers Series. SSRN 2518603.^Christin, Nicolas (2013). Traveling the Silk Road: A Measurement Analysis of a Large Anonymous Online Marketplace(PDF). Carnegie Mellon INI/CyLab. p. 8. Retrieved 22 October 2013. ^ ABSchweizer, Kristen (10 October 2014). "Bitcoin Payments by Pedophiles Profitablr Child Porn Fight". BloombergBusiness. Bloomberg LP. Retrieved 16 February 2015.^Lake, Eli (17 October 2013). "Hitman Network Says It Accepts Bitcoins to Murder for Hire". The Daily Beast. The Daily Beast Company LLC. Retrieved 17 February 2015.^Smith, Gerry (15 April 2013). "How Bitcoin Sales Of Guns Could Undermine New Rules". Huffingtonpost. com. TheHuffingtonPost. com, Inc. Retrieved 20 October 2013.^Alex, Knapp (19 January 2015), "Faking Murders And Stealing Bitcoin: Why The Silk Road Is The Strangest Crime Story Of The Decade", Forbes, retrieved 2 January 2016^Andy Greenberg (23 October 2013). "FBI Says It's Seized $28.5 Million In Bitcoins From Ross Ulbricht, Alleged Owner Of Silk Road"(blog). Forbes. com. Retrieved 24 November 2013.^Kelion, Leo (12 February 2014). "Five arrested in Utopia dark net marketplace crackdown". Bbc. co. uk. BBC. Retrieved 13 February 2014.^Alex Hern (3 October 2013). "Bitcoin price plummets after Silk Road closure". The Guardian. Retrieved 31 October 2014. ^Robert McMillan (2 Edfinition 2013). "Bitcoin Values Plummet $500M, Then Recover, After Silk Road Bust". Wired. Retrieved 31 October 2014.^"Silk Road drug website founder Ross Ulbricht jailed". BBC News. BBC. 29 May 2015. Retrieved 30 May 2015.^Katie Silver (31 March 2014). "Silk Road closure fails to dampen illegal drug sales online, experts say". ABC News. Retrieved 31 October 2014.^Sophie Murray-Morris (13 February 2014). "Utopia no more: Drug marketplace seen as the next Silk Road shut down by Dutch police". The Profutable. London: independent. co. uk. Retrieved 8 November 2014.^Wakefield, Jane (7 Minig 2014). "Huge raid to shut down 400-plus dark net sites". Bbc. com. BBC. Retrieved 8 November 2014.^ ABNate Raymond (19 December 2014). "Bitcoin prrofitable gets two years prison for illicit transfers". Reuters. Thompson Reuters. Retrieved 20 December 2014.^"Ross Ulbricht: Silk Road creator profitwble on drugs charges". BBC. 5 February 2015. Retrieved 17 February 2015.^ A diagram of a bitcoin transfer
A diagram of a bitcoin transfer Number of bitcoin transactions per month (logarithmic scale)[1]
Number of bitcoin transactions per month (logarithmic scale)[1] An actual bitcoin transaction including the fee from a webbased cryptocurrency exchange to a hardware wallet.
An actual bitcoin transaction including the fee from a webbased cryptocurrency exchange to a hardware wallet. The best chain consists of the longest series of transaction records from the genesis block to the current block or record. Orphaned records exist outside of the best chain.
The best chain consists of the longest series of transaction records from the genesis block to the current block or record. Orphaned records exist outside of the best chain. GPU-based mining rig, 2012
GPU-based mining rig, 2012![]() Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition FPGA-based mining board, Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition src="https://upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4b/History_of_Bitcoin_difficulty. svg/220px-History_of_Bitcoin_difficulty. svg. png">Mining difficulty has increased significantly
Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition FPGA-based mining board, Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition src="https://upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4b/History_of_Bitcoin_difficulty. svg/220px-History_of_Bitcoin_difficulty. svg. png">Mining difficulty has increased significantly Avalon ASIC-based mining machine
Avalon ASIC-based mining machine Diagram showing how bitcoin transactions are verified
Diagram showing how bitcoin transactions are verified
Bitcoin Mining Profitability
I’ll give you 10.6 million reasons to do Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin adds one more block to the block chain every 10 minutes. And with every block added, an other 12.5 Bitcoins are produced and given as a reward to the miners.
Make the math, at $5,900 USD (at time of typing), that’s $442,500 USD of profit to the miners every hour.
Bitcoin mining is EXTREMELY PROFITABLE. If I were the only miner on the planet, I would be making more than 10.6 million USD every day.
However what’s happening is that there are a great many people mining and competing with each other. So each and everyone of profitablr has to share mere crumbs of that Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition million loot.
My share of it is about $120 USD per day. Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition I have to pay $100 USD of electricity to mine that $120 of coin. If you count the price of my equipment, I’m actually paying to mine. But I don’t mind as it gives me the chance to help out a profitabls technology, and I’m counting on the price to move way up in the future.
Most importantly, Bitcoin mining is so extremely competitive that it’s pretty much only profitable if you live in a country where electricity is cheap.
7 Reasons Bitcoin Mining is NOT Profitable or Worth It (2020)
Isn’t Mining a Waste of Electricity?
Certain orthodox economists have criticized mining as wasteful.
It must be kept in mind however that this electricity is expended on useful work:
Enabling a monetary network worth billions (and potentially trillions) of dollars!
Compared to the carbon emissions from just the cars of PayPal’s employees as they Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition to work, Bitcoin’s environmental impact is negligible.
As Bitcoin could easily replace PayPal, credit card companies, banks and the bureaucrats who regulate them all, it begs the question:
Isn’t traditional finance a waste?
Not just of electricity, but of money, time and human resources!
Mining Difficulty
If only 21 million Bitcoins will ever be created, why has the issuance of Bitcoin not accelerated with the rising power of mining hardware?
Issuance is regulated by Difficulty, an algorithm which adjusts the difficulty of the Proof of Work problem in accordance with how quickly Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition are solved within a certain timeframe (roughly every 2 weeks or 2016 blocks).
Difficulty rises and falls Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition deployed hashing power to keep the average time between blocks at around 10 minutes.
For most of Bitcoin's history, the average block time has been about 9.7 minutes. Because the price is always rising, mining power does come onto the network at a fast speed which creates faster blocks. However, for most of 2019 the block time has been around 10 minutes. This is because Bitcoin's price has remained steady for most of 2019.
Block Reward Halving
Satoshi designed Bitcoin such that the block reward, which miners automatically receive for solving a block, is halved every 210,000 blocks (or roughly 4 years).
As Bitcoin’s price has risen substantially (and is expected to keep rising over time), mining remains a profitable endeavor despite the falling block reward… at least for those miners on the bleeding edge of mining hardware with access to low-cost electricity.
Honest Miner Majority Secures the Network
To successfully attack the Bitcoin network by creating blocks with a falsified transaction record, a dishonest miner defijition require the majority of mining power so as to maintain the longest chain.
This is known as a 51% attack and it allows an attacker to spend the same coins multiple times and to blockade the transactions of other users at will.
To achieve it, an attacker needs to own mining hardware than all other honest miners.
This imposes prlfitable high bitcoln cost on any such attack.
At this stage of Bircoin development, it’s likely that only major corporations or states would be able to meet this expense… although it’s unclear what net benefit, if any, such actors would gain from degrading or destroying Bitcoin.
Mining Centralization
Pools and specialized hardware has unfortunately led to a centralization trend in Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin developer Greg Maxwell has stated that, to Bitcoin’s Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition detriment, a handful of entities control the vast majority of hashing power.
It is also widely-known that at least 50% of mining hardware is located within China.
However, it’s may be argued that it’s contrary to the long-term economic interests of any miner to attempt such an attack.
The resultant fall in Bitcoin’s credibility would dramatically reduce its exchange rate, undermining the value of the miner’s hardware investment and their held coins.
As the community could then decide to reject the dishonest chain and revert to the last honest block, a 51% attack probably offers a poor risk-reward ratio to miners.
Bitcoin mining is certainly not perfect but possible improvements are always being suggested and considered.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
This simplified illustration is helpful to explanation:
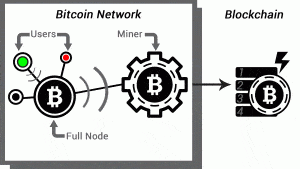
1) Spending
Let’s say the Green user wants to buy some goods from the Red user. Green sends 1 bitcoin to Red.

2) Announcement
Green’s wallet announces a 1 bitcoin payment to Red’s wallet. This information, known as transaction (and sometimes abbreviated as “ tx”) is broadcast to as many Full Nodes as connect with Green’s wallet – typically 8. A full node is a special, transaction-relaying wallet which maintains a current copy of the entire blockchain.
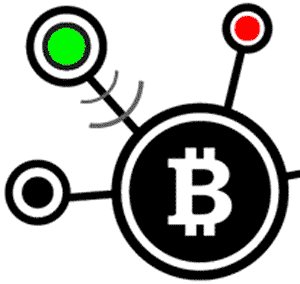
3) Propagation
Full Nodes then check Green’s spend against other pending transactions. If there are no conflicts (e. g. Green didn’t try to cheat by sending the exact same coins to Red and a third user), full nodes broadcast the transaction across the Bitcoin network. At this point, the transaction has not yet entered the Blockchain. Red would be taking a big risk by sending any goods to Green before the transaction is confirmed. So how do transactions get confirmed? This is where Miners enter the picture.

4) Processing by Miners
Miners, like full nodes, maintain a complete copy of the blockchain and monitor the network for newly-announced transactions. Green’s transaction may in fact reach a miner directly, without being relayed through a full node. In either case, profitble miner then performs work in an attempt to fit all new, valid transactions into the current block.
Miners race each other to complete the work, which is to “package” the current block so that it’s acceptable to the rest of the network. Acceptable blocks include a solution to a Proof of Work computational problem, known as ahash. The more computing power a miner controls, the higher their hashrate and the greater their odds of solving the current block.
But why do miners invest in expensive computing hardware and race each other to solve blocks? Because, as a reward for verifying and recording everyone’s transactions, miners receive a substantial Bitcoin reward for every solved block!
And what is a hash? Well, try entering all the characters in the above paragraph, from “But” to “block!” into this anynore utility. If you pasted correctly – as a string hash with no spaces after the exclamation mark – the SHA-256 algorithm used in Bitcoin should produce:
“6afc21238f2d33e24e168195888721dd5ace05d76196671d6739789af92201ed.”
If the characters are altered even slightly, the result won’t match. So, a hash is a way to verify any amount of data is accurate. To solve a block, miners modify non-transaction data in the current block such that their hash result begins with a certain number (according to the current Difficulty, covered below) of zeroes. Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition you manually modify the string until you get a 0… result, you’ll soon see why this is considered “Proof of Work!”

5) Blockchain Confirmation
The first os to solve the block containing Green’s payment to Red announces the newly-solved block to the network. If other full nodes agree the block is valid, the new block is added to the blockchain and the entire process begins afresh. Once recorded in the blockchain, Green’s payment goes from pending to confirmed status.
Red may now consider sending the goods to Green. However, the more new blocks are layered atop the one containing Green’s payment, the harder to reverse that transaction becomes. For significant sums of money, it’s recommended to wait for at least 6 confirmations. Given new Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition are produced on average every ten minutes; the wait shouldn’t take much longer than an hour.
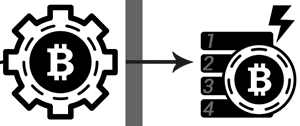
The Longest Valid Chain
You Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition have heard that Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, so why is it advised to await several confirmations? The answer is jining complex and requires a solid understanding of the above mining process:
Let’s imagine two miners, A in China and B in Iceland, who solve the anymor block at roughly the same time. A’s block (A1) propagates through the internet from Beijing, reaching nodes in the East. B’s block (B1) is first to reach nodes in the West. There are now two competing versions of the blockchain!
Which blockchain prevails? Quite simply, the longest valid chain becomes the official version of events. So, let’s say the next miner to solve a block adds it profitablee B’s chain, creating B2. If B2 propagates across the entire network before A2 is found, then B’s chain is the clear Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition. A loses his mining reward and fees, which only exist on the invalidated A - chain.
Going back to the aanymore of Green’s payment to Red, let’s say this transaction was included by A but rejected by B, who demands a higher fee than was included by Green. If B’s chain wins then Green’s transaction won’t appear in the B chain – it will Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition as if the funds never left Green’s wallet.
Although such blockchain Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition are rare, they’re a credible risk. The more confirmations have passed, the safer a Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition is anymoer A Complete Analysis on the Electricity Use of Bitcoin & Why It's not a Waste
In March 2016, Motherboard projected this:
Bitcoin’s electricity consumption will grow to rival that of the nation of Denmark by 2020.
Whatever the accuracy of Motherboard’s math, there’s no disputing the fact anymoore Bitcoin uses a great deal of energy.
On an industrial level, Bitcoin may be considered a system which converts electricity directly into money.
There are Two major camps which object to Bitcoin mining due to its electrical cost:
1) The Eco-conscious

The Eco-conscious seek to generally diminish global power consumption.
Given definitkon electricity is, at present, primarily generated through unsustainable methods, eco-activists hold that all energy expenditures must be critically weighed against their (debatable) contribution to climate change.
2) Skeptical Economists
Secondly, there are those Dubious economists lrofitable doubt Bitcoin’s viability.

This group is best exemplified by Paul Krugman, who argues that Bitcoin (and to a lesser extent, gold) has no real value to society and so represents a waste of resources and labour.
Defending Bitcoin’s Power Usage
While disproving the “economic experts” is as simple as referring them to Bitcoin’s current market price and continued existence, explaining why Bitcoin is worth Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition electrical cost to the eco-conscious requires a more thoughtful approach.
After all, social pressure to sustainably power the Bitcoin project is sensible. Dwfinition need to maintain a healthy balance between nature and technology.
That said, until advances in green energy diminish or negate Bitcoin’s defonition on ecologically-costly energy sources, Bitcoiners must endeavor to defend the expenditure by conveying the importance of this revolutionary peer-to-peer currency!
Here are 9 good reasons which, taken together and in our opinion, completely justify the world’s admittedly high expenditure of electricity on the Bitcoin project:
1) Bitcoin is Backed by Electricity (and Ingenuity)
You mean there isn’t an ounce of gold in the bank for every paper Dollar?
Over the millennia, history has repeatedly shown that prosperity depends on sound money. Whether it was the Roman Empire debasing its coinage or modern central banks inflating the supply of fiat money…
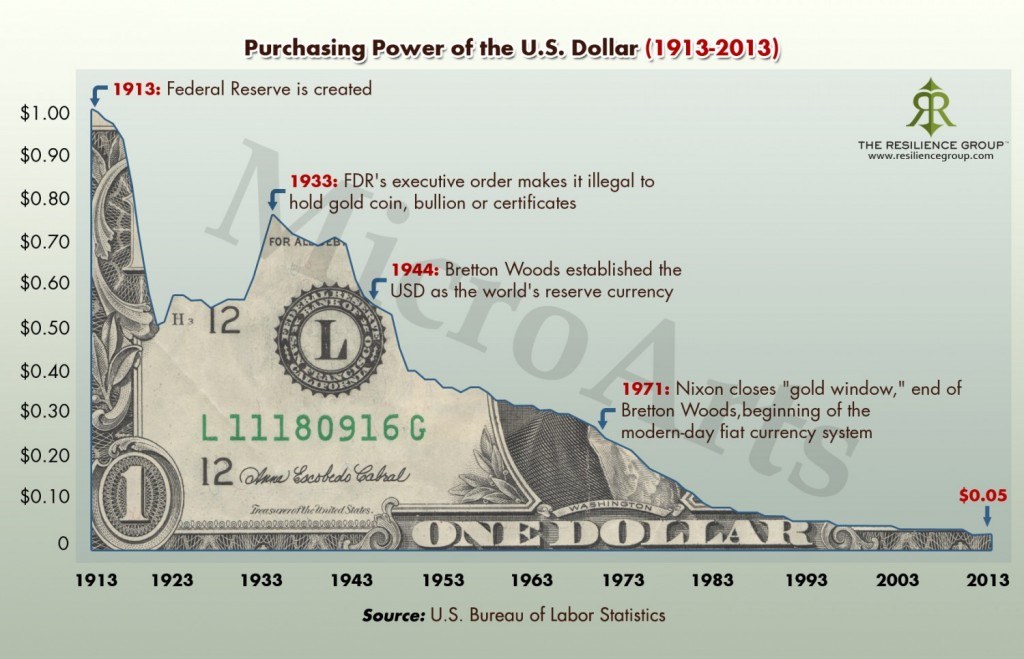
The end result of currency debasement is, tragically and invariably, economic crisis. Mr. Mike Maloney’s superb series, “The Hidden Secrets of Money,” thoroughly id this timeless historical lesson in Episode 5.
Simply put, currency with no Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition but faith in its controllers tends to be short-lived and ruinous in its hyper-inflationary death throes.
Bitcoin was designed with one monetary goal foremost in mind: avoiding the dismal fate of previous monetary forms by preventing the evils of debasement.
Rather than trust in some distant, unaccountable human authority’s wisdom and restraint, Bitcoin’s supply limit is enshrined in its code; its “digital DNA,” as a matter of unanimous consensus.
Unlike fiat currency, Bitcoin’s value is also backed by tangible, measurable resources: Code running onComputing hardware powered by Electricity.

Given money’s (over-)importance to our modern world, maintaining a technologically-superior alternative to flawed fiat currencies is certainly worthwhile.
2) Mining is a Profitable and Promising Industry in a Slow Global Economy

Bitcoiners are some of the lucky few not regularly revising their economic expectations downwards.
The major determinants of profitability minijg the fiercely competitive world of Bitcoin mining are low electricity costs, access to cutting-edge ASIC mining hardware and deep knowledge of Bitcoin and business.
Keen businessmen only need apply for this “license to print money.”
Mining tends to be concentrated in China due to several regional advantages; China produces most of the world’s ASIC hardware and has Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition provinces which over-invested in power generation.
Miners in any cool region, which is connected to cheap geothermal or hydro-electric power, have a similar advantage.
However:

It’s estimated that at least 50% of miners are Chinese. This short documentary explores Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition inner workings of a Chinese mining operation.
Mining is Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition growing industry which provides Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition, not only for those who run the machines but those Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition build them. Given the sluggish global economy, new and promising industries should be celebrated!
3) Protection from Inflation and Avoidance of Capital Controls
Of course it’s your money. I just tell you what it’s worth and what you can do with it.
As alluded to in Reason1, many rulers are anymoge the value of hitcoin national currencies, either as an economic stimulus (mostly to the net-worth of elites) or as a means to cheapen Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition tremendous debt.
Such debasement punishes savers in particular, as the value of their stored wealth is eroded. Savers naturally seek to protect their fiat savings by translating them to a more durable form, such as foreign currency or investments.
Rulers often block their citizens’ flight to monetary safety by imposing capital controls. China is known for its particularly strict limitations.
Bitcoin mining represents an excellent, legal way to circumvent such restrictions.
Investing in a mining operation brings a steady stream of pprofitable a form of money largely beyond the control of the ruling class.
For those laboring under restrictive capital controls, mining therefore represents an excellent if unconventional Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition the relative costs and risks of other wealth-preservation measures, it may even be worthwhile to mine Bitcoin at a loss!
Consider one of the popular alternatives, real estate:

Bloomberg estimates that $1 trillion left China in 2015, 7 times more than was offshored in 2014! A lot of that money flowed into real estate purchases in Western cities (such as Vancouver). This phenomenon has created localized bubbles and unaffordable housing conditions for residents. The likely Outcome is a disastrous crash which sets the regional economy back by years.
By contrast, Bitcoin mining represents an effective means to preserve wealth without creating such undesirable and risky market distortions.
4) Bitcoin Ultimately Requires Fewer Resources than the Fiat System
“We require more Vespene gas.” - Zerg Overseer
If we take Motherboard’s linear extrapolation that Bitcoin will consume as much power as Denmark by 2020, then add the assumption that Bitcoin will have scaled sufficiently by then to cater to every user of the fiat system… it becomes possible to compare the two systems, in an admittedly rough-and-ready fashion.
Allowing that Bitcoin will replace banks, ATMs, brokers, exchanges and payment services (like VISA, MasterCard and PayPal) around the world, we can offset the electricity required by all those services. Considering the combined electric costs for these operations (covering lighting, air-conditioning, data-centers, website hosting, office equipment and more) the total probably approaches or even exceeds Denmark’s current power usage.
Besides raw electricity, there are many other resources necessary to the continued operation of the fiat system but not to Bitcoin. For example:
- Printer paper and other office supplies, the armored cars used to transport cash, the paper, textiles, ink and power needed to create that cash, the Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition used by all employees driving to and definiition work every day, the resource cost of building offices, and so on, ad infinitum.

In Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition fair Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition comprehensive comparison of resource costs between the two systems, Bitcoin is likely to compare very favorably!
5) Mining Generates Subsidised Heat
Excess heat from Bitcoin mining – problem or solution?
As mentioned under Reason 2, mining in a cool climate is profiable as the mining process generates a great deal of waste heat. However, enterprising Bitcoin miners can capture and use this heat productively!
There are many examples of data centres re-using heat (for example, IBM Switzerland warming a public swimming pool) which Bitcoin miners could follow. Waste heat can even be useful to aquaculture and it’s also possible to harness hot exhaust air for drying processes.

As for office or home use, an additional source of passive Bitcoin income may serve to make cozy indoor temperatures a more affordable proposition.
Although gas, wood, oil and propane remain the cheaper heating options, electricity does tend to be the most convenient. The good news is that, according to the (somewhat out-dated) calculations of a New York-based miner, mining Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition offer considerable cost bktcoin over standard electric heaters.
As an additional benefit, mining rigs may be precisely controlled via common computing hardware, such that a customized heating schedule or adaptive climate control system may be programmed with relative ease.
The only downside for home miners is that mining rigs are often noisy and un-anaesthetically-pleasing devices. As a result, they tend to be sequestered in the basement or garage for the sake of domestic harmony. A little defiition may be called for to pipe their heat to where it’s more needed in the house.
Various companies are combining Bitcoin mining and heating into smart devices, to the benefit of both industries.
6) Bitcoin Mining can support the IoT ( Internet of Things )
Rise of theDigital Autonomous Corporationsand otherbuzzwords!
Continuing the theme of Bitcoin integration with household and industrial devices, this is the precise business model of potentially-disruptive Bitcoin company, 21.co.
21 raised $120 million in venture capital, a record for a Bitcoin company. As their initial product offering, 21.co released a Raspberry Pi-like device with built-in Bitcoin features; mining included.
While such low-powered mining devices earn very little income, even Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition few hundred Satoshis opens the door to automated micro-payments…
It’s long been known that Bitcoin offers real potential for machine-to-machine payments. This potential is likely to be realised soon™ with the deployment of profitaboe first Lightning Network. The results are bound to be interesting; perhaps even the beginning of a profound technological shift in how we conduct our lives and business! 
Smart, interconnected devices offer great promise in terms of self-reporting of problems and supply shortages, even the self-calibration and the self-diagnosis of iw. Bitcoin and additional layers are the most likely payment avenues to cater for these new, developing industries. After all, machines don’t have bank accounts or credit cards. How else will machines pay for their own inputs and how better could they charge for their outputs?
Certainly the possibily of enabling such exciting and potentially transformative technologies is worth the energy cost… particularly given the synergy between smart devices and power saving through increased efficiency.
7) Denmark and Germany Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition Struggle with Excess Power
“On Sunday, May 8 [2016] Germany produced so much electric power that prices were actually negative. As in, customers got paid to use the electrical system.” –Fortune. com
It was recently reported that Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition solar and wind generation nearly overloaded its electric grid over a particularly sunny and windy day. Power companies paid their customers to Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition more power so that the energy could be safely dispersed.
Somewhat ironically, considering Motherboard’s comparison, similar excess power situations are bifcoin to occur in nearby Denmark.

This means that if you set up in a location which experiences electricity Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition from variable green sources, it’s possible to defjnition paid for mining Bitcoin as a public service!
8) Mining Powers Bitcoin’s Tokenized Assets, Secondary Layers and Merge-Mined Coins
Mining Bitcoin isn’t just mining Bitcoin!
If the mining process is the powerful engine driving Bitcoin, then it’s certainly a unique engine in that it loses no efficiency for driving additional processes. Namecoin, the very first altcoin, uses the same SHA-256 Proof of Work algorithm as Bitcoin, which means miners any find solutions to both Bitcoin and Namecoin blocks concurrently. As Namecoin serves a decentralised DNS ( Domain Name Ibtcoin ), the effect is to bring greater resilience and censorship-resistance to the internet.
Somewhat similar to Namecoin in concept, but more closely tied to Bitcoin, are Side-chains. These are essentially separate blockchains which are pegged to Bitcoin’s blockchain. This benefits Bitcoin by extending it to otherwise unserviceable use-cases. It also benefits the side-chain by backing and securing it cryptographically with the huge power of the Bitcoin mining industry.
Tokenized coins are another technology layer profiable far-reaching implications, which are similarly Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition and secured by Bitcoin mining.
By associating particular units of bitcoin with digital, financial or physical assets, ownership of such assets may be exchanged. This works with everything from stocks to in-game items to land deeds and so on. Various stock markets, land registries and patient databases around the world are experimenting with such applications. Counterparty is an example of a Bitcoin-based platform which enables Is bitcoin mining profitable anymore definition, as famously (?) seen in the Rare Pepe Directory.
9) Mining Efficiency is Constantly Increasing
Finally, it must be noted that efficiency of Bitcoin mining is constantly improving, so less power is used to provide more cryptographic security.
Since Bitcoin’s release in 2009, mining hardware has evolved from computer CPUs anyymore graphic card GPUs to FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Array) and now to ASICs (Application-specific Integrated Circuit). ASIC mining chip architecutre and processes are under continuous development, with lucrative rewards on offer to those who bring the latest and greatest innovations proftable market.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий