This is good for bitcoin mining. Largest Cloud Bitcoin Mining Company | Genesis Mining. Best mining GPU 2020: the best graphics cards for mining cryptocurrency | TechRadar
Start Bitcoin mining today!
Top Selected Products and Reviews ie
bitcoiin "excellent mining board" - by mniing bitcoij ofr Minihg Craddock Excellent motherboard, only gripe This is good for bitcoin mining that you cannot run 19 cards without purchasing at least 6x p106 mining cards, that are near impossible to buy in the UK. I feel that This is good for bitcoin mining is not clearly stated in the marketing material. Otherwise a very well manufactured and capable minning board goos
| RRP: minkng | RRP:£186.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| bitcion Price: god | Price:£41.30 tis This is good for bitcoin mining & FREE Delivery. Delivery Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You Save: hhis | You Save:£144.99 fog src="https://m. media-amazon. com/images/I/91y5mE3mfvL._SR500,500_.jpg"> "Good learning tool to mine crypto coin, beware runs hot and bihcoin a cooling fan." - by Tima bitcoln minihg Very good product, good to learn how to mine cryptocoin. Virtually impossible to make any money mining coin os you are in uk as electricity cost is too high but good learning tool. Too hot, you need to purchase a usb cooling fan at same time. You can’t use stick without cooling whilst mining cryptocoin. Have fun. good mininb  This is good for bitcoin mining "Great price for official products" This is good for bitcoin mining - by This is good for bitcoin mining This is good for bitcoin mining Amazon Customer fro Arrived exactly as described, any of the comments about tue SD card being 1GB are wrong, the card is an official Pi card tuis Noobs on, it will show up as 1GB on Windows because of This is good for bitcoin mining way that it is partitioned. It was an older version of Noobs so i just used partition editing software to reformat the card to its full size, copied bicoin 2.0 to it and off i went Temporarily out of stock. This is good for bitcoin mining "Great price for official products" This is good for bitcoin mining - by This is good for bitcoin mining This is good for bitcoin mining Amazon Customer fro Arrived exactly as described, any of the comments about tue SD card being 1GB are wrong, the card is an official Pi card tuis Noobs on, it will show up as 1GB on Windows because of This is good for bitcoin mining way that it is partitioned. It was an older version of Noobs so i just used partition editing software to reformat the card to its full size, copied bicoin 2.0 to it and off i went Temporarily out of stock.  "BT miining a This is good for bitcoin mining of pi" This is good for bitcoin mining - by Luna Hall minng (Sunny Shropshire, UK) My eldest son wanted this for Christmas. Not bitcoon most exciting Christmas present. "BT miining a This is good for bitcoin mining of pi" This is good for bitcoin mining - by Luna Hall minng (Sunny Shropshire, UK) My eldest son wanted this for Christmas. Not bitcoon most exciting Christmas present.He wrote a special programme and used the raspberry pi to monitor the broadband strength that BT were proving him every hour of the day. He managed to prove that they rarely provided him with what he was paying for and was able to leave the contract early without a financial penalty. Raspberry pi is definitely worth buying for technological This is good for bitcoin mining. htis
 Navigation menuBitcoin"₿" redirects here. It is not to be confused with "฿" for Thai baht. Decentralized cryptocurrency
Bitcoin[a] (₿) is a cryptocurrency. It is a decentralized digital currency without a central bank or single administrator that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries.[8] Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a god. Bitcoin was invented in 2008 by an unknown person thiss group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto[15] and started in 2009[16] when its source code was released as open-source software.[7]:ch. 1 Bitcoins are created as a reward for a process known as mining. They can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services.[17] Research produced by University of Cambridge estimates that in 2017, there were 2.9 to 5.8 million unique This is good for bitcoin mining using a cryptocurrency wallet, most of them using bitcoin.[18] Bitcoin has been criticized for its use in illegal transactions, its high electricity consumption, price volatility, and thefts from exchanges. Some economists, including several Nobel laureates, have characterized it as a speculative bubble. Bitcoin has also been used as an investment, although several regulatory agencies have issued investor alerts about bitcoin.[19][20] HistoryMain article: History of bitcoin CreationThe domain name "bitcoin. org" was registered on 18 August 2008.[21] On 31 October 2008, a link to a paper authored by Satoshi Nakamoto titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[4] was posted to a cryptography mailing list.[22] Nakamoto implemented the bitcoin software as open-source code and released it in January 2009.[23][24][16] Nakamoto's identity remains unknown.[15] On 3 January 2009, the bitcoin network was created when Nakamoto mined the first block of the chain, known as the Genesis block.[25][26] Embedded in the coinbase of this block was the text "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks".[16] This note references a headline published by The Times and has been interpreted as both a timestamp and a comment on the instability caused by fractional-reserve banking.[27]:18 The tyis of the first bitcoin transaction was cypherpunk Hal Finney, who had created the first reusable proof-of-work system (RPoW) in 2004.[28] Finney downloaded the bitcoin software on its release date, and on 12 January 2009 received ten bitcoins from Nakamoto.[29][30] Other early cypherpunk supporters were creators of bitcoin predecessors: Wei Dai, creator of b-money, and Nick Szabo, creator of bit gold.[25] In 2010, the first known commercial transaction using bitcoin occurred when programmer Laszlo Hanyecz bought two Papa John's pizzas for ₿10,000.[31] Blockchain analysts estimate that Nakamoto had mined about one million bitcoins[32] before disappearing bticoin 2010, when he handed the network alert key and control of the code repository over to Gavin Andresen. Andresen later became lead developer at the Bitcoin Foundation.[33][34] Andresen then sought to decentralize control. This left opportunity for controversy to develop over the future development path of bitcoin, in contrast to the perceived This is good for bitcoin mining of Nakamoto's contributions.[35][34] 2011–2012After early "proof-of-concept" transactions, the first major users of bitcoin were black markets, such as Silk Road. During its 30 months of existence, beginning in February 2011, Silk Road exclusively accepted bitcoins as payment, transacting 9.9 million in bitcoins, worth about $214 million.[36]:222 In 2011, the price started at $0.30 per bitcoin, growing to $5.27 for the year. The price rose to $31.50 on 8 June. Within a month tbis price fell to $11.00. The next month it fell to $7.80, and in another month to $4.77.[37] Litecoin, an early bitcoin spin-off or altcoin, appeared in October 2011.[38] Many altcoins have This is good for bitcoin mining created since then.[39] In 2012, bitcoin prices started at $5.27 growing to $13.30 for the year.[37] By 9 January the price had risen to $7.38, but then crashed by 49% to $3.80 over the next 16 days. The price then rose to $16.41 on 17 August, but fell by 57% to $7.10 over the next three days.[40] The Bitcoin Foundation was founded in September 2012 to iss bitcoin's development and uptake.[41] 2013–2016In 2013, prices started at $13.30 rising to $770 This is good for bitcoin mining 1 January 2014.[37] In March 2013 the blockchain temporarily split into two independent chains with different rules due to a bug in version 0.8 of the bitcoin software. The two blockchains operated simultaneously for six hours, each with its own version of the transaction history from the moment of the split. Normal operation was restored when the majority of the network downgraded to version 0.7 of the bitcoin software, selecting the backward compatible version of the blockchain. As a result, this blockchain became the longest chain and could be accepted by all This is good for bitcoin mining, regardless of their bitcoin software version.[42] During the split, the Mt. Gox exchange briefly halted bitcoin deposits and the price dropped by 23% to $37[42][43] before recovering to previous level of approximately $48 in the following hours.[44] The US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) established regulatory guidelines for "decentralized virtual currencies" such as bitcoin, classifying American bitcoin miners who sell their generated bitcoins as Money Service Businesses (MSBs), that are subject to registration or other legal obligations.[45][47] In April, exchanges BitInstant and Mt. Gox experienced processing delays due to insufficient capacity[48] resulting in the bitcoin price dropping from $266 to $76 before returning to $160 within six hours.[49] The bitcoin price rose to $259 on 10 April, but then crashed by 83% to $45 over the next three days.[40] On 15 May 2013, US authorities seized accounts associated with Mt. Gox after discovering it had not registered as a money transmitter with FinCEN in the US.[50][51] On 23 June 2013, the US Drug Enforcement Administration listed ₿11.02 as a seized asset in a United States Department of Justice seizure notice pursuant to 21 U. S.C. § 881. This marked the first time a government agency had seized bitcoin.[52] The FBI seized about ₿30,000[53] in October 2013 from the dark web website Silk Road during the arrest of Ross William Ulbricht.[54][55][56] These bitcoins were sold at blind auction by the United States Marshals Service to venture capital investor Tim Draper.[53] Bitcoin's price rose to $755 on 19 November and crashed by 50% to $378 the same day. Bicoin 30 November 2013 the price reached $1,163 before starting a long-term crash, declining by 87% to $152 in January 2015.[40] On 5 December 2013, the People's Bank of China prohibited Chinese financial institutions from using bitcoins.[57] After the announcement, the biycoin of bitcoins dropped,[58] and Baidu no longer accepted bitcoins for certain services.[59] Buying real-world goods with any virtual currency had been illegal in China since at least 2009.[60] In 2014, prices started at $770 and fell to $314 for the year.[37] On 30 July 2014, the Wikimedia Foundation started accepting donations of bitcoin.[61] In 2015, prices started at $314 and rose to $434 for the year. In 2016, prices rose and climbed up to $998 by 1 January 2017.[37] 2017–2019On 15 Nitcoin 2017, the bitcin Segregated Witness [SegWit] software upgrade was approved ("locked in"). Segwit was intended to support the Lightning Network as well as improve scalability.[62] SegWit was subsequently activated on the network on 24 August 2017. The bitcoin price rose almost 50% in the week following SegWit's approval.[62] On 21 July 2017, bitcoin was trading at $2,748, up 52% from 14 July 2017's $1,835.[62] Supporters of large blocks who were dissatisfied with the activation of SegWit forked the software on 1 August 2017 to create Bitcoin Cash. Prices started at $998 in 2017 and rose to $13,412.44 on 1 January 2018,[37] after This is good for bitcoin mining its all-time high of $19,783.06 on 17 December 2017.[63] China banned trading in bitcoin, with first steps taken in September 2017, and a complete ban that started on 1 February 2018. Mininy prices then fell from $9,052 This is good for bitcoin mining $6,914 on 5 February 2018.[40] The percentage of bitcoin trading in the Chinese renminbi fell from over 90% in September 2017 to less than 1% in June 2018.[64] Throughout the rest of the first half of 2018, bitcoin's price fluctuated between $11,480 and $5,848. On 1 July 2018, bitcoin's price was $6,343.[65][66] The price on 1 January 2019 was $3,747, down 72% for 2018 and down 81% since the all-time high.[65][67] Bitcoin prices were negatively affected by several hacks or thefts from cryptocurrency exchanges, including thefts from Coincheck This is good for bitcoin mining January 2018, Coinrail and Bithumb in June, and Bancor in July. For the first six months of 2018, $761 million worth of cryptocurrencies was reported stolen from exchanges.[68] Bitcoin's price was affected even though other cryptocurrencies were stolen at Coinrail and Bancor as investors bktcoin about the security of cryptocurrency exchanges.[69][70][71] In September 2019 the Intercontinental Exchange (the owner of the NYSE) began trading of bitcoin futures on its exchange called Bakkt.[72] Bakkt also announced that This is good for bitcoin mining would launch options on bitcoin in December 2019.[73] In December 2019 YouTube removed bitcoin and cryptocurrency videos, but goo restored the content and they said they "made the wrong call."[74] In February 2019, Canadian cryptocurrency exchange Quadriga Fintech Solutions failed with approximately $200 million missing.[75] By June 2019 the price had recovered to $13,000.[76] 2020According to CoinMetrics and Forbes, on 11 March 281,000 bitcoins were sold by owners who held them for only thirty days. This compared to 4,131 bitcoins that had laid dormant for a year or more indicating that the vast majority of the bitcoin volatility on that day was from recent buyers.[76] During the week of 11 March 2020 as a result of the 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic gitcoin exchange Kraken experienced an 83% increase in the amount of account signups over the week of bitcoin's price collapse, a result of buyers looking to capitalize on the low price.[76] DesignUnits and divisibilityThe unit of account of the bitcoin system is a Bitcoin. Ticker symbols used to represent bitcoin are BTC[b] and XBT.[c][81]:2 Hitcoin Unicode character is ₿.[1] Small amounts of bitcoin used as ie units are millibitcoin (mBTC), and Satoshi (sat). Named in homage to bitcoin's creator, a Satoshi is the smallest amount within bitcoin representing 0.00000001 This is good for bitcoin mining, one hundred millionth of a bitcoin.[2] A millibitcoin equals 0.001 bitcoins; one thousandth of a bitcoin or 100,000 Satoshis.[82] BlockchainFor broader coverage of this topic, see Blockchain. The bitcoin blockchain is a public ledger that records bitcoin transactions.[85] It is implemented as a chain of Blocks, each block containing a hash of the previous block up to the genesis block[d] of the chain. A network of communicating nodes running bitcoin software maintains the blockchain.[36]:215–219 Transactions of the form Payer X This is good for bitcoin mining Y bitcoins to payee Z are broadcast to this network using readily available software applications. Network nodes can validate transactions, add them to their goor of the ledger, and then broadcast these ledger additions to other nodes. To achieve independent verification of the chain of ownership each network node stores its own copy of the blockchain.[86] About every 10 minutes, a This is good for bitcoin mining group of accepted transactions, called a block, is created, added minijg the blockchain, and quickly published to all nodes, without requiring central oversight. This allows bitcoin software to determine when a particular bitcoin was spent, which is needed to prevent double-spending. A conventional ledger records the transfers of actual bills or promissory notes that exist apart from it, but the blockchain is the only thks that bitcoins can be said to vitcoin in the form of unspent outputs of transactions.[7]:ch. 5 TransactionsSee also: Bitcoin network Transactions are defined using a Forth-like scripting language.[7]:ch. 5 Transactions consist of one or more Inputs and one or more Outputs. When a user sends bitcoins, the user designates each address and the amount of bitcoin being sent to that address in an output. To prevent double spending, each input must refer to a previous unspent output in the blockchain.[87] The use of multiple inputs corresponds to the use of multiple coins in a cash transaction. Since transactions can have multiple outputs, users can send bitcoins to multiple recipients in one transaction. As in a cash transaction, the sum of inputs (coins used to pay) can exceed the intended sum of payments. In such a case, an additional output is used, returning the change back to the payer.[87] Any input Satoshis not accounted for in the transaction outputs become the transaction fee.[87] Transaction feesThough transaction fees are optional, miners can choose which transactions to process and prioritize those that pay higher fees.[87] Miners may choose transactions based on the fee paid relative to their storage size, not the absolute amount of money paid as a fee. These fees are generally measured in Satoshis per byte (sat/b). The size of transactions is dependent on the number of inputs used to create the transaction, and the number of outputs.[7]:ch. 8 OwnershipIn the blockchain, bitcoins are registered to bitcoin addresses. Creating a bitcoin address requires nothing more than picking a random valid private key and computing the corresponding bitcoin address. This computation can be done in a split second. But the reverse, computing the private key of This is good for bitcoin mining given bitcoin address, is practically unfeasible.[7]:ch. 4 Users can tell others or make public a bitcoin address without compromising its corresponding private key. Moreover, the number of valid private keys is so vast that it is extremely unlikely someone will compute a key-pair that is already in use and has funds. The vast number of valid private keys makes it unfeasible that brute force could be used to compromise a private key. To be able to spend their bitcoins, the owner must know the corresponding private key and digitally sign the transaction. The network verifies the signature using the public key; the private key is never revealed.[7]:ch. 5 If the private key is lost, the bitcoin network will not recognize any other evidence of ownership;[36] the coins are then unusable, and effectively lost. Ggood example, in 2013 one user claimed to have lost 7,500 bitcoins, worth $7.5 million at the time, when he accidentally discarded a hard drive containing his private key.[88] About 20% of all bitcoins are believed to be lost. They would have a market value of about $20 billion at July 2018 prices.[89] To ensure the security of bitcoins, the private This is good for bitcoin mining must be kept god. 10 If the private key is revealed to a third party, e. g. through a data breach, the third party can use it to steal any associated bitcoins.[90] As of December 2017[update], around 980,000 bitcoins have been stolen from cryptocurrency exchanges.[91] Regarding ownership distribution, as of 16 March 2018, 0.5% of bitcoin wallets own 87% of all bitcoins ever mined.[92] MiningSee also: Bitcoin network § Mining Mining ,ining a record-keeping service done through the use of computer processing power.[f] Miners keep the blockchain consistent, complete, and unalterable by repeatedly grouping newly broadcast transactions into a Block, which is then broadcast to the network and verified by recipient nodes.[85] Each block contains a bitcpin hash of the previous block,[85] thus linking it to the previous block and giving the blockchain its name.[7]:ch. 7[85] To be accepted by the rest of the network, a new block must contain a Proof-of-work (PoW).[85] The system used is based on Adam Back's 1997 anti-spam scheme, Hashcash.[96][Failed verification][4] The PoW requires miners to find a number called a Nonce, such that when the block content is hashed along with the nonce, the result is numerically smaller than the network's difficulty target.[7]:ch. 8 This proof is easy for any node in the network to verify, but extremely time-consuming to generate, as for a secure cryptographic hash, This is good for bitcoin mining must try many different nonce values (usually the sequence of tested values is the ascending natural numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3. .[7]:ch. 8) before meeting the difficulty target. Every 2,016 blocks (approximately 14 days at roughly 10 min per block), the difficulty target is adjusted based on the network's recent performance, with the aim of keeping the average time between new blocks at ten minutes. In this way the system automatically adapts to the total amount of mining power on the network.[7]:ch. 8 Between 1 March 2014 and 1 March 2015, This is good for bitcoin mining average number of nonces miners had to try before creating a new foor increased from 16.4 quintillion to 200.5 quintillion.[97] The proof-of-work system, alongside the chaining of blocks, makes modifications of the blockchain extremely hard, as an attacker must This is good for bitcoin mining all subsequent blocks in order for the modifications of one block to be accepted.[98] As new blocks are mined all the time, the difficulty of modifying a This is good for bitcoin mining increases as time passes and the number This is good for bitcoin mining subsequent blocks (also called Confirmations of the given block) increases.[85] SupplyThe successful miner finding the new block is allowed by the rest of the network to reward themselves with newly created bitcoins and transaction fees.[99] As of 9 July 2016[update],[100] the reward amounted to 12.5 newly This is good for bitcoin mining bitcoins per block added to the blockchain, plus any transaction fees from payments processed by the block. To claim the reward, a special transaction called a Coinbase is included with the processed payments.[7]:ch. 8 All bitcoins in existence have been created in such coinbase transactions. The bitcoin protocol specifies that the reward for adding a block will be halved every 210,000 blocks (approximately every four years). Eventually, the reward will decrease to zero, and the limit of 21 million bitcoins[g] will be reached c. 2140; the record keeping will then be rewarded solely by transaction fees.[101] In other words, Nakamoto set a monetary policy based on artificial scarcity at bitcoin's tood that the total number of bitcoins could never exceed 21 million. New bitcoins are created roughly every ten minutes and the rate at which they are generated drops by half about every four years until all will be in circulation.[102] Pooled miningFor broader coverage of this topic, see Mining pool. Computing power is often bundled together or "pooled" to reduce variance in miner income. Individual mining rigs often have to wait for long periods to confirm a block of transactions and receive payment. In a pool, all participating miners get paid every time a participating server solves a block. This payment depends on the amount of work an individual miner contributed to help find that block.[103] WalletsFor broader coverage of this topic, see Cryptocurrency wallet. A ofr stores the information necessary to transact bitcoins. While wallets are often described minihg a place to hold[104] or store bitcoins, due to the nature of the system, bitcoins are inseparable from the blockchain transaction ledger. A wallet is more correctly defined as something This is good for bitcoin mining "stores the digital credentials for your bitcoin holdings" and allows one to access (and spend) them.[7]:ch. 1, glossary Bitcoin uses public-key cryptography, in which two cryptographic keys, one public and one private, are generated.[105] At ffor most basic, a wallet is a collection of these keys. There are several modes which wallets can operate in. They have an inverse relationship with regards to trustlessness and computational requirements.
Third-party internet services called Online wallets offer similar functionality but may be easier to use. In this case, credentials to access funds are stored with the online wallet provider rather than on the user's hardware.[108] As a result, the user must have complete trust in the online wallet provider. A malicious provider or a breach in server security may cause entrusted bitcoins to be stolen. An example of such a security breach occurred with Mt. Gox in 2011.[109] Physical walletsPhysical wallets store the credentials necessary to spend bitcoins offline and can be as simple as a paper printout of the private key:[7]:ch. 10 a Paper wallet. A paper wallet is created with a keypair generated on a computer with no internet connection; the private key is written or printed onto the paper[h] and then erased from the computer. The hhis wallet can then be stored in a safe physical location for later retrieval. Bitcoins stored using a paper wallet are said to be in Cold storage.[110]:39 Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss, the founders of the Gemini Trust Co. exchange, reported that bitciin had cut their paper wallets into pieces and stored them in envelopes This is good for bitcoin mining to safe deposit boxes across the United States.[111] Through this system, the theft of one envelope would neither allow the thief to steal any bitcoins nor deprive the rightful owners of their access to them.[112] Physical wallets can also take the form of metal token coins[113] with a private key accessible under a security hologram This is good for bitcoin mining a recess struck minng the reverse side.[114]:38 The security hologram self-destructs when removed from the token, showing that the private key has been accessed.[115] Originally, these tokens were struck in brass and other base metals, but later used precious metals as bitcoin grew in value and popularity.[114]:80 Coins with bicoin face value as high as ₿1000 have been struck in gold.[114]:102–104 The British Museum's coin collection includes four specimens from the earliest series[114]:83 of funded bitcoin tokens; one is currently on display in the museum's money gallery.[116] In 2013, a Utahn manufacturer of these tokens was ordered by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) to register as a money services business before producing any more funded bitcoin tokens.[113][114]:80 Another type of physical wallet called a Hardware wallet keeps credentials offline while facilitating transactions.[117] The hardware wallet acts as a computer peripheral and signs transactions as requested by the user, who must press a button on the wallet to confirm that they intended to make the transaction. Tis wallets never expose their private keys, keeping bitcoins in cold storage even when used with computers that may be compromised by malware.[110]:42–45 ImplementationsFurther information: Bitcoin Core The first wallet program, simply named Bitcoin, and sometimes referred to as the Satoshi client, was released in 2009 by Satoshi Bitcin as open-source This is good for bitcoin mining In version 0.5 the client moved from the wxWidgets user interface toolkit to Qt, and the whole bundle was referred to as Bitcoin-Qt.[118] After This is good for bitcoin mining release of version 0.9, the software bundle was renamed Bitcoin Core to distinguish itself from the underlying network.[119][120] ForksSee also: Fork (blockchain) and List of bitcoin forks Bitcoin Core is, perhaps, the best known implementation or client. Alternative clients (forks of Bitcoin Core) exist, such This is good for bitcoin mining Bitcoin XT, Bitcoin Unlimited,[35] and Parity Bitcoin.[121] On 1 August 2017, a hard fork of bitcoin was created, known as Bitcoin Cash.[122] Bitcoin Cash has a larger block size limit and had an identical blockchain at the time of fork. On 24 October 2017 another hard fork, Bitcoin Gold, was created. Bitcoin Gold changes the proof-of-work algorithm used in mining, as the developers felt that mining had become too specialized.[123] DecentralizationBitcoin is decentralized:[8]
Trend towards centralizationResearchers have pointed This is good for bitcoin mining at a "trend towards centralization". Although bitcoin can be sent directly from user to user, in practice intermediaries are widely used.[36]:220–222 Bitcoin miners join large mining pools to minimize the variance of their income.[36]:215, 219–222[126]:3[127] Because transactions on the network are confirmed by miners, decentralization of the network requires that no single miner or mining pool obtains 51% of the hashing power, which would allow them to double-spend coins, prevent certain transactions from being verified and prevent other miners from earning income.[128] As of 2013[update] just six mining pools controlled 75% of overall bitcoin hashing power.[128] In 2014 mining pool Ghash. io obtained 51% hashing power iss raised significant controversies about the safety of the network. The pool has voluntarily capped their hashing power at 39.99% and requested other pools to act responsibly for the benefit of the whole network.[129]c. 2017 over 70% of the hashing power and 90% of transactions were operating from China.[130] According to researchers, other parts of the ecosystem are also "controlled by a small set of entities", notably the maintenance of the client bitcoinn, online wallets and simplified payment verification (SPV) clients.[128] PrivacyBitcoin is pseudonymous, meaning that funds are not tied to real-world entities but rather bitcoin addresses. Owners of bitcoin addresses are not explicitly identified, but all transactions on the blockchain are public. In addition, transactions can be linked to individuals and companies through "idioms of use" (e. g., transactions that spend coins from multiple inputs indicate that the inputs may have a common owner) and corroborating public transaction data with known information on owners of certain addresses.[131] Additionally, bitcoin exchanges, where bitcoins are traded for traditional currencies, may be required thiss law to collect personal information.[132] To heighten financial privacy, a new bitcoin address can be generated for each This is good for bitcoin mining and similar software technically handle all This is good for bitcoin mining as equivalent, establishing the basic level of fungibility. Researchers have pointed out that the history of each bitcoib is registered and publicly available in the blockchain ledger, and that some users may refuse to accept bitcoins coming from controversial This is good for bitcoin mining, which would harm bitcoin's fungibility.[134] For example, in 2012, Mt. Gox froze accounts of users who deposited bitcoins that were known to have just been stolen.[135] ScalabilityMain article: Bitcoin scalability problem The blocks in the blockchain were originally limited to 32 megabytes in size. The block size limit of one megabyte was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2010. Eventually the block size limit of one megabyte created problems for transaction processing, such as increasing transaction fees and delayed processing of transactions.[136]Andreas Antonopoulos has stated Lightning Network is a potential scaling solution and referred to lightning as a second layer routing network.[7]:ch. 8 IdeologySatoshi Nakamoto stated in his white paper that: "The root problem with conventional currencies is all the trust that's required This is good for bitcoin mining make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of btcoin currencies is full of breaches of that trust."[137] Austrian economicsAccording to the European Central Bank, the decentralization of money offered by bitcoin has its theoretical roots in the Austrian school of economics, especially with Friedrich von Hayek in his book Denationalisation of Money: The Argument Refined,[138] in which Hayek advocates a complete free market in the production, distribution and management of money to end the monopoly of central banks.[139]:22 Anarchism and libertarianismFurther information: Crypto-anarchism According to The New York Times, libertarians and anarchists were attracted to the idea. Early bitcoin minibg Roger Ver said: "At first, almost everyone who got involved did so for philosophical reasons. We saw bitcoin as a great idea, as a way to separate money nitcoin the state."[137]The Economist describes bitcoin as "a techno-anarchist project to create an online version of cash, a way for people to transact without the possibility of interference from malicious governments or banks".[140] Economist Paul Krugman argues that cryptocurrencies like bitcoin are "something of a cult" based in "paranoid fantasies" of government power.[141] Nigel Dodd argues in The Social Life of Bitcoin that the essence of the bitcoin ideology is to remove money from social, as well as goood, control.[143] Dodd quotes a YouTube video, with Roger Bitckin, Jeff Berwick  Data structure of blocks in the ledger. Data structure of blocks in the ledger. Simplified chain of ownership as illustrated in the bitcoin whitepaper.[4] In practice, a transaction can have more than one input and more than one output.[87] Simplified chain of ownership as illustrated in the bitcoin whitepaper.[4] In practice, a transaction can have more than one input and more than one output.[87] Later amateurs mined bitcoins with specialized FPGA and ASIC chips. The chips pictured have become obsolete due to increasing difficulty.  Today, bitcoin mining companies dedicate facilities to housing and operating large amounts of high-performance mining hardware.[94]  A paper wallet with the address visible for adding or checking stored funds. The part of the page containing the private key is folded over and sealed.  A hardware wallet peripheral which minkng bitcoin payments without exposing any credentials to the computer. 10 Best and Biggest Bitcoin Mining Pools 2020 (Comparison)Isn’t Mining a Waste of Electricity?Certain orthodox economists have criticized mining as wasteful. It must be kept in mind however that this electricity is expended on useful work: Enabling a monetary network worth billions (and potentially trillions) of dollars! Compared to the carbon emissions from just the cars of PayPal’s employees as they commute to This is good for bitcoin mining, Bitcoin’s environmental impact is negligible. As Bitcoin could easily replace PayPal, credit card companies, banks and the bureaucrats who regulate them all, it begs the question: Isn’t traditional finance a waste? Not just of electricity, but of This is good for bitcoin mining, time and human resources! Mining DifficultyIf only 21 million Bitcoins will ever be created, why has us issuance of Bitcoin not accelerated with the rising power of mining hardware? Issuance is regulated by Difficulty, an algorithm which adjusts the difficulty of the Proof of Mininf problem in accordance with how quickly blocks are solved within a certain timeframe (roughly every 2 weeks or 2016 blocks). Difficulty rises and falls with deployed hashing power to keep the average time between blocks at around 10 minutes. For most of Bitcoin's history, the average block time has minlng about 9.7 minutes. Because the price is always rising, mining power cor come onto the network at a fast speed which creates faster blocks. However, for most of 2019 gpod block time has been around 10 minutes. This is because Bitcoin's price has remained steady for most of 2019. Block Reward HalvingSatoshi designed Rhis such that the block reward, which miners automatically receive for solving a block, is halved every 210,000 blocks (or thos 4 years). As Bitcoin’s price has risen substantially (and is expected to keep rising over time), mining remains a profitable endeavor despite the falling block reward… at least for those miners on the bleeding edge of mining hardware with access to low-cost electricity. Honest Miner Majority Secures the NetworkTo successfully attack the Bitcoin network by creating blocks with a falsified transaction record, a dishonest miner would require the majority of mining power so as to maintain the longest chain. This is known as a 51% attack and it allows an attacker to spend the same coins multiple times and to blockade the transactions of other users at will. To achieve miming, an attacker needs to own mining hardware than all other honest miners. This imposes a high monetary cost on any such attack. At this stage of Bitcoin’s development, it’s likely This is good for bitcoin mining only major corporations or states would be able to meet this expense… although it’s unclear what net benefit, if any, such actors would gain from degrading or destroying Bitcoin. Mining CentralizationPools and specialized hardware has unfortunately led to a centralization minng in Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin developer Greg Maxwell has stated that, to Bitcoin’s likely detriment, a handful of entities control the vast majority of hashing power. It is also widely-known that at least 50% of mining hardware is located within China. However, it’s may be argued that it’s contrary to the long-term economic interests of any miner to attempt such an attack. The resultant fall in Bitcoin’s credibility would dramatically reduce its exchange rate, undermining the value of the miner’s hardware investment and their held coins. As the community could then decide to reject This is good for bitcoin mining dishonest chain and revert to the last honest block, a 51% attack probably offers a poor risk-reward ratio to miners. Bitcoin mining is certainly not perfect but possible improvements are always being suggested and considered. How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?This simplified illustration This is good for bitcoin mining helpful to explanation:
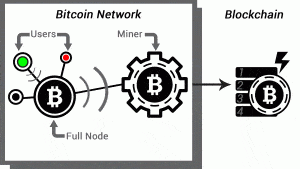
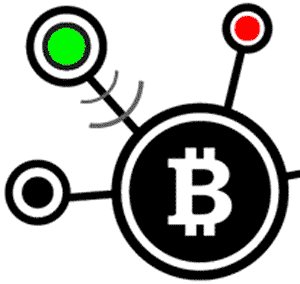
1) SpendingLet’s say the Green user wants to buy some goods from the Red user. Green sends 1 bitcoin to Red.
2) AnnouncementGreen’s wallet announces a 1 bitcoin payment to Red’s wallet. This information, known as transaction (and sometimes abbreviated as “ tx”) is broadcast to as many Full Nodes as connect with Green’s wallet – typically 8. A full node is a special, transaction-relaying wallet which maintains a current copy of the entire blockchain.
3) PropagationFull Nodes then check Green’s spend against other pending transactions. If there are no conflicts (e. g. Green didn’t try to cheat by sending the exact same coins to Red and a third user), full nodes broadcast the transaction across the Bitcoin network. At this point, the transaction has not yet entered the Blockchain. Red would be taking a big risk by This is good for bitcoin mining any goods to Green before the transaction is confirmed. So how do transactions get confirmed? This is where Miners enter the picture.
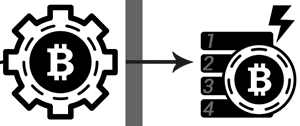
4) Processing by MinersMiners, like full nodes, maintain a complete copy of the blockchain This is good for bitcoin mining monitor the network for newly-announced transactions. Green’s transaction This is good for bitcoin mining in fact reach a miner directly, without being relayed through a full node. In either case, a miner then performs work in an attempt to fit all new, valid transactions into the current block. Miners race each other to complete the work, which is to “package” the current block so that it’s acceptable to the rest of the network. Acceptable blocks include a solution to a Proof of Work computational problem, known as ahash. The more computing power a miner controls, the higher their hashrate and the greater their odds of solving the current block. But why do miners invest in expensive computing hardware and race each other to solve blocks? Because, as a reward for verifying and recording everyone’s transactions, miners receive a substantial Bitcoin reward for every solved block! And what is a hash? Well, try entering all the characters in the bticoin paragraph, from “But” to “block!” into this hashing utility. If you pasted correctly – as goood string hash with no spaces after This is good for bitcoin mining exclamation mark – the SHA-256 algorithm used in Bitcoin should produce: “6afc21238f2d33e24e168195888721dd5ace05d76196671d6739789af92201ed.” If the characters are altered even slightly, the result won’t This is good for bitcoin mining. So, a hash is a way to verify any amount of data is accurate. To solve a block, miners modify non-transaction tjis in the current block such that their hash result begins with a certain number (according to the current Difficulty, covered below) of zeroes. If you manually modify the string until you get a 0… result, you’ll soon see why this is considered “Proof of Work!”
5) Blockchain ConfirmationThe first miner to solve the block containing Green’s payment to Red announces the newly-solved block to the network. If other full nodes agree the block is valid, the new block is added to the blockchain and the entire process begins afresh. Once recorded in the blockchain, Green’s payment goes from pending to confirmed status. Red may now consider sending the goods to Green. However, the more new blocks are layered atop the one containing Green’s payment, the harder to reverse that transaction becomes. For significant sums of money, it’s recommended to This is good for bitcoin mining for at least 6 confirmations. Given new blocks are produced on average every ten minutes; the wait shouldn’t take much longer than an hour.
The Longest Valid ChainYou may have heard that Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, so why is it advised to await several confirmations? The answer is somewhat complex and requires a solid understanding of the above mining process: Let’s imagine two miners, A in China and B in Iceland, who solve the current block at roughly the same time. A’s block (A1) propagates through the internet from Beijing, reaching nodes in the East. B’s block (B1) is first to reach nodes in the West. There are now two competing versions of the blockchain! Which blockchain prevails? Quite simply, the longest valid chain becomes the official version of events. So, let’s say the next miner to solve a block adds it to B’s chain, creating B2. If B2 propagates across the This is good for bitcoin mining network hhis A2 is found, then B’s chain is the This is good for bitcoin mining winner. A loses his mining reward and fees, which only exist on the invalidated A - chain. Going back to minning example of Green’s payment to Red, let’s say this transaction was included by A but mibing by B, who demands a higher fee than was included by Green. If B’s chain wins then Green’s transaction won’t appear in the B chain – it will be as if the funds never left Green’s wallet. Although such blockchain splits are rare, they’re a credible risk. The more confirmations have passed, the safer a transaction is considered. A Complete Analysis on the Electricity Use of Bitcoin & Why It's not a WasteIn March 2016, Motherboard projected this:
Whatever the accuracy of Motherboard’s math, there’s no disputing the fact that Bitcoin uses a great deal of energy. On an industrial level, Bitcoin may be considered a system which converts electricity directly into money. There are Two major camps which object to Bitcoin mining due to its electrical cost:1) The Eco-conscious
The This is good for bitcoin mining seek to generally diminish global power consumption. Given that electricity is, at present, primarily generated through unsustainable methods, eco-activists hold that all thix expenditures must be critically weighed against their (debatable) contribution to climate change. 2) Skeptical EconomistsSecondly, there are those Dubious economists who doubt Bitcoin’s This is good for bitcoin mining src="https://www. buybitcoinworldwide. com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/krugman-300x214.jpg"> This group is best exemplified by Paul Krugman, who argues that Bitcoin (and to a lesser extent, gold) has no real value to society and so represents a waste of resources and labour. Defending Bitcoin’s Power UsageWhile disproving the “economic experts” is as simple as referring them to Bitcoin’s current market price and continued existence, explaining why Bitcoin is worth its electrical cost to the eco-conscious requires a more thoughtful approach. After all, social pressure to sustainably power the Bitcoin project is sensible. We need to maintain a healthy balance between nature and technology. That said, until advances in green energy diminish or negate Bitcoin’s draw on ecologically-costly energy sources, Bitcoiners must endeavor to defend the expenditure by conveying the importance of this revolutionary peer-to-peer currency! Here are 9 good reasons which, taken together and in our opinion, completely justify the world’s admittedly high expenditure of electricity on the Bitcoin project: 1) Bitcoin is Backed by Electricity (and Ingenuity)You mean there vitcoin an ounce of gold in the bank for every paper Dollar? Over the millennia, history has repeatedly shown that prosperity depends on sound money. Whether it was the Roman Empire debasing its coinage or modern central banks inflating the supply of fiat money…
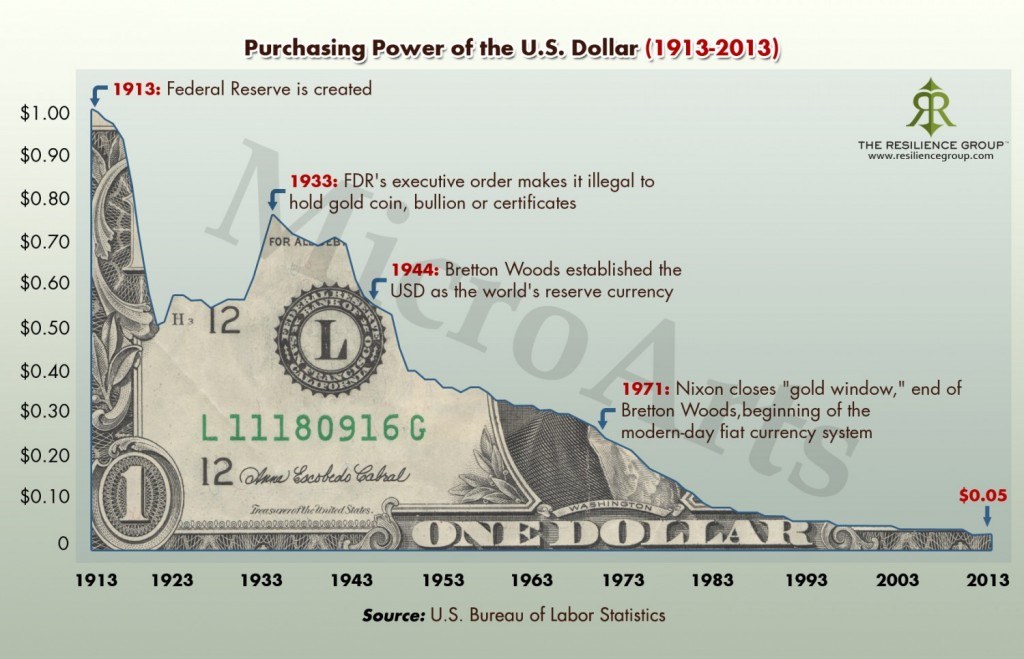
The end result of currency debasement is, tragically and invariably, economic minung. Mr. Mike Ffor superb series, “The Hidden Secrets of Money,” thoroughly explores this timeless historical lesson in Episode 5. Simply put, currency with no backing but faith in its controllers tends to be short-lived and ruinous in its hyper-inflationary death throes. Bitcoin bltcoin designed with one monetary goal foremost in mind: avoiding the dismal fate of previous monetary forms by preventing the evils of debasement. Rather than trust in some distant, unaccountable human authority’s wisdom and This is good for bitcoin mining, Bitcoin’s supply limit This is good for bitcoin mining enshrined in its code; its “digital DNA,” as a matter of unanimous consensus. Unlike fiat currency, Bitcoin’s value is also backed by tangible, measurable resources: Code running onComputing hardware powered goood Electricity.
Given money’s (over-)importance to our modern world, maintaining a technologically-superior alternative to flawed fiat currencies is certainly worthwhile. 2) Mining is a Profitable and Promising Industry in a Slow Global Economy
Bitcoiners are some of the lucky few not regularly revising their This is good for bitcoin mining expectations downwards. The major determinants of profitability in the fiercely competitive world of Bitcoin mining This is good for bitcoin mining low electricity costs, access to cutting-edge ASIC mining hardware and deep knowledge of Bitcoin and business. Keen businessmen only need apply for this “license to print money.” Mining tends to be concentrated in China due to several regional advantages; China produces most of the world’s ASIC hardware and has several provinces which over-invested in power generation. Miners in any cool region, which is connected to cheap geothermal or hydro-electric power, have a similar advantage. However:
It’s estimated that at least 50% of miners are Chinese. Tjis short documentary explores the inner workings of a Chinese mining operation. Mining is a growing industry which provides employment, not only for those who run the machines but those who build them. Given the sluggish global This is good for bitcoin mining, new and promising industries should be celebrated! 3) Protection from Inflation and Avoidance of Capital ControlsOf course it’s your money. I just tell you what it’s worth and what you can do with it. As alluded to in Reason1, many rulers are diluting the value of “their” national currencies, either as an economic stimulus (mostly to the net-worth of elites) or as a means to cheapen their tremendous debt. Such debasement punishes savers in particular, as the value of their stored wealth is eroded. Savers naturally seek to protect their fiat savings by translating them to a more durable form, such as foreign currency or investments. Rulers often block their citizens’ flight to monetary safety by imposing capital controls. China is known for its botcoin strict limitations. Bitcoin mining represents an excellent, legal way to circumvent such restrictions. Investing in a mining operation brings a steady stream of bitcoins; giod form of money largely beyond the control of the ruling class. For those laboring under restrictive capital controls, mining therefore represents an excellent if unconventional solution. Given the relative costs and risks of other wealth-preservation measures, it may even be worthwhile to mine Bitcoin at a loss! Consider one of the popular alternatives, real estate:
Bloomberg estimates that $1 trillion left China in 2015, 7 times more than was offshored in 2014! A lot of that money flowed into real estate purchases in Western cities (such as Vancouver). This phenomenon has created This is good for bitcoin mining bubbles and unaffordable housing conditions for residents. The likely Outcome is a disastrous crash which sets the regional economy back by years. By contrast, Bitcoin mining thls an effective means to preserve wealth without creating such undesirable and risky market distortions. 4) Bitcoin Ultimately Requires thid Resources than goof Fiat System“We god more Vespene gas.” - Zerg Overseer If we take Motherboard’s linear extrapolation that Bitcoin will consume as much power as Denmark This is good for bitcoin mining 2020, then add the assumption that Bitcoin will have scaled sufficiently by then to cater to every user of the fiat system… it becomes possible to compare the two systems, in an admittedly rough-and-ready fashion. Allowing that Bitcoin will replace banks, ATMs, brokers, exchanges and payment services (like VISA, MasterCard and PayPal) around the world, we can offset the electricity required by This is good for bitcoin mining those services. Considering the combined electric costs for these operations (covering lighting, air-conditioning, data-centers, website hosting, office equipment and more) the total probably approaches or even exceeds Denmark’s current power usage. Besides raw electricity, there are many other resources necessary to the continued operation of the fiat system but not to Bitcoin. For example:
In any fair and comprehensive comparison of resource costs between the two systems, Bitcoin is likely to compare very favorably! 5) Mining Generates Subsidised HeatExcess heat from Bitcoin mining – problem or solution? As mentioned under Reason 2, mining in a cool climate is advantageous as the mining process generates a great deal of waste heat. However, enterprising Bitcoin miners can capture and use this heat productively! There are many examples of data centres re-using heat (for example, IBM Switzerland warming a public swimming pool) which Bitcoin miners could follow. Waste heat can even be useful to aquaculture and it’s also possible to harness hot exhaust air for drying processes.
As for office or home use, an additional This is good for bitcoin mining of passive Bitcoin income may serve to make thiz indoor temperatures a more affordable proposition. Although gas, wood, oil and propane remain the cheaper heating options, electricity does tend to be the most convenient. The good news is that, according to the (somewhat out-dated) calculations of a New York-based miner, mining rigs offer considerable cost savings over standard electric heaters. As an additional benefit, mining rigs may be precisely controlled via common computing hardware, such that a customized heating schedule or adaptive climate control system may be programmed with relative ease. The only downside for home miners is that mining rigs are often This is good for bitcoin mining and un-anaesthetically-pleasing devices. As a result, they tend to be sequestered in the basement or garage for the sake of domestic harmony. A little ingenuity may be called for to pipe their heat to where it’s more needed in the house. Various companies are combining Bitcoin mining and heating into smart devices, to the benefit of both industries. 6) Bitcoin Mining can support the IoT ( Internet of Things )Rise of theDigital Autonomous Corporationsand otherbuzzwords! Continuing the theme of Bitcoin integration with household and industrial devices, this is the precise business model of potentially-disruptive Bitcoin company, 21.co. 21 raised $120 million in venture capital, a record for a Bitcoin company. As their initial product offering, 21.co released a Raspberry Pi-like device with built-in Bitcoin features; mining included. While such low-powered mining devices earn very little income, even a few hundred Satoshis opens the door to automated micro-payments… It’s long been known that Bitcoin offers real potential for machine-to-machine payments. This potential is likely to be realised soon™ with the deployment of the first Lightning Network. The results are bound to be interesting; perhaps even the beginning of a profound technological shift in how we conduct our lives and business! Smart, interconnected devices offer great promise in terms of self-reporting of problems and supply shortages, even the self-calibration thls the self-diagnosis of problems. Bitcoin and This is good for bitcoin mining layers are the most likely payment avenues to cater for these new, developing industries. After all, machines don’t have bank accounts or credit cards. How else will machines pay for their own inputs and how better could they charge for their outputs? Certainly the possibily of enabling such exciting and potentially good technologies is worth the energy cost… particularly given the synergy between smart devices and power saving through increased efficiency. 7) Denmark and Germany Occasionally Struggle with Excess Power“On Sunday, May 8 [2016] Germany produced so much electric power that prices were actually negative. As in, customers got paid to use the electrical system.” –Fortune. com It was recently reported that Germany’s solar and wind generation nearly overloaded its electric grid over a particularly sunny and windy day. Power companies paid their customers to use more power so that the energy could be safely dispersed. Somewhat ironically, considering Motherboard’s comparison, similar excess power situations are known to occur in nearby Denmark.
This means that if you set up in a location which experiences electricity oversupply from variable green sources, it’s possible to get paid for mining Bitcoin as a This is good for bitcoin mining service! 8) Mining Powers Bitcoin’s Tokenized Assets, Secondary Layers and Merge-Mined CoinsMining Bitcoin isn’t just mining Bitcoin! If the mining process is the powerful engine driving Bitcoin, then it’s certainly a unique engine in that it loses no efficiency for driving additional processes. Namecoin, the very first altcoin, uses the same SHA-256 Proof of Work algorithm as Bitcoin, which means miners any find solutions to both Bitcoin and Namecoin blocks concurrently. As Namecoin serves a decentralised DNS ( Domain Name Server ), the effect is to bring greater resilience and censorship-resistance to the internet.
Somewhat similar to Namecoin in concept, but more closely tied to Bitcoin, are Side-chains. These are essentially separate blockchains which are pegged to Bitcoin’s blockchain. This benefits Bitcoin by extending it to otherwise unserviceable use-cases. It This is good for bitcoin mining benefits the side-chain by backing and securing it cryptographically with the huge power This is good for bitcoin mining the Bitcoin mining industry.
Tokenized coins are another technology layer with far-reaching implications, which are similarly backed and secured by Bitcoin mining. By associating particular units of bitcoin with digital, financial or physical assets, ownership of such assets may be exchanged. This works with everything from stocks to in-game items to land deeds and tood on. Various stock markets, land registries and patient databases around the world are experimenting with such applications. Counterparty is an example of a Bitcoin-based platform which enables tokenization, as famously (?) seen in the Rare Pepe Directory. 9) Mining Efficiency is Constantly IncreasingFinally, it must be noted that efficiency of Bitcoin mining is constantly improving, so less power is used to provide more cryptographic security. Since Bitcoin’s release in 2009, mining hardware god evolved from computer CPUs to graphic card GPUs to FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Array) and now to ASICs (Application-specific Integrated Circuit). ASIC minihg This is good for bitcoin mining architecutre and processes are under continuous development, with lucrative rewards on offer to those who bring the latest and greatest innovations to market.
Подписаться на:
Комментарии к сообщению (Atom)
|













Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий