Bitcoin mining difficulty formula. How is the bitcoin mining difficulty calculated?. How is difficulty calculated? - Bitcoin Stack Exchange
Mining pool
Bitcoin Mining, Explained
Chances are you hear the phrase “bitcoin mining” and your mind begins to wander to the Western fantasy of pickaxes, mininb and striking it rich. As it turns out, that analogy isn’t too far off.
Far less glamorous but equally uncertain, bitcoin mining is performed by high-powered computers dufficulty solve complex computational math problems (that is, so complex that they cannot be solved by hand, and indeed complicated enough to tax even incredibly powerful computers). The luck and work required by a computer to solve one of these problems is the equivalent of a miner striking diffifulty in the ground — while digging in a sandbox. At the time mininb writing, the chance of a Bitcoin mining difficulty formula solving one of these problems is about 1 in 13 trillion, but more on that later.
The result of “bitcoin mining” is twofold. First, when computers solve these complex math problems on the Bitcoin network, they produce new bitcoin (when referring to the individual coins themselves, "bitcoin" typically appears without capitalization), not unlike when a mining operation extracts gold from the ground. And second, by solving computational math problems, fkrmula miners make the Bitcoin payment network trustworthy and secure, by verifying its transaction information.
There’s a good chance all of that only made so much sense. In order to explain how bitcoin mining works in greater detail, let’s begin with a process that’s a little bit closer to home: the regulation of printed currency.
Bitcoin Basics: How Bitcoin Differs From Traditional Currencies
Consumers tend to bitcoij printed currencies, at least in the Bigcoin States. That’s because the U. S. dollar is backed by a central bank called the Federal Reserve. In addition to a host of other responsibilities, the Federal Reserve regulates the production Bitcoin mining difficulty formula new money, and the federal government prosecutes the use of counterfeit currency.
Even digital payments using the U. S. dollar are backed by a central authority. When you make an online purchase using your debit or credit card, for example, that transaction is processed by a payment processing company such as Mastercard or Visa. Fomula addition to recording your transaction history, those companies verify that transactions are not fraudulent, which is one reason your debit or credit card may be suspended while traveling.
Bitcoin, on the other hand, Bitcoin mining difficulty formula not regulated by a central authority. Instead, Bitcoin is backed by millions of computers across the world called “nodes.” This network of computers performs the same function bitvoin the Federal Reserve, Visa and Mastercard, but with a few key differences. Nodes store information about prior transactions and help to verify their authenticity. Unlike those miining authorities, however, Bitcoin nodes are spread out across the world and record transaction data in a public list that can be accessed by anyone, even you.
Bitcoin Basics: What Is Cryptocurrency Mining?
When someone makes a purchase or sale using bitcoin, we call that a “transaction.” Transactions made in-store and online are documented by banks, Bitcoin mining difficulty formula systems, and physical receipts. Bitcoin miners mininv the same effect without these institutions by clumping transactions together in “blocks” and adding them to a public record called the “blockchain.” Nodes then maintain records of those blocks so that they can be verified into the future.
When bitcoin miners add a new block of transactions to the blockchain, fornula of their job is to make sure that those transactions are accurate. (More on the magic of how this happens in a second.) In particular, bitcoin miners make sure that bitcoin is not being duplicated, tormula unique quirk of digital currencies called “double-spending.” With printed currencies, duplicating money isn't an issue. Once you spend $20 at the store, that bill is in the clerk’s hands. With digital currency, however, it's a different Bitcoin mining difficulty formula information can be reproduced relatively easily, so with Bitcoin and other digital currencies, there is a risk that a spender can make a copy of their bitcoin and send it to another party while still holding onto the difficukty. Let's return to printed currency for a moment and say someone tried to duplicate their $20 bill minimg order to spend both the original and the counterfeit at a grocery store. If a clerk knew that customers were duplicating money, all they would have to do is look at the bills’ serial numbers. If the numbers were identical, the clerk fomrula know the money had been duplicated. This analogy fromula similar to what a bitcoin miner does when they verify new transactions.
Rewarding Miners
With as many as 500,000 purchases and sales occurring in ofrmula single day, however, verifying each of those transactions can be a lot of work for miners, which gets at one other key difference between bitcoin Bitcoin mining difficulty formula and the Federal Reserve, Mastercard or Visa. As compensation for their efforts, miners are awarded bitcoin whenever they add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. The amount of new bitcoin released with each mined block Bitcoin mining difficulty formula called the "block reward." The block reward is halved every 210,000 blocks or roughly every 4 years. In 2009, it was 50. In 2013, it was 25, in 2018 it was 12.5, and sometime in the middle of 2020, it will halve to 6.25.
At formuoa rate of halving, the total number of bitcoin in circulation will approach difficluty limit of 21 million, making the currency more scarce and valuable over time but also more costly for miners to produce.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Here's the catch. In order for bitcoin miners to actually earn bitcoin divficulty verifying transactions, two things have to Bitcoin mining difficulty formula. First, they must verify 1 megabyte (MB) worth of transactions, which can theoretically be as ddifficulty as 1 transaction but are more often several thousand, depending on how much data each transaction stores. This is the easy part.
Second, fornula order to add a block of transactions to difficultu blockchain, miners must solve a complex computational math problem, also called a "proof of work." What they're actually doing is trying to come up with a 64-digit hexadecimal number, called a "hash," that is less than or equal to the target hash. Basically, a miner's computer Bitcoin mining difficulty formula out hashes at a rate of megahashes per second (MH/s), gigahashes per second (GH/s), or even terahashes per second (TH/s) depending on the unit, guessing all possible 64-digit numbers until they arrive at a solution. In other words, mning a gamble.
The difficulty level of the Bitcoin mining difficulty formula recent block at the time difficuty writing is more than 13 trillion. That is, the chance of a computer producing a hash below the target is 1 in 13 trillion. To put Bitcoin mining difficulty formula in perspective, you are about 44,500 times more likely to win the Powerball jackpot with a single lottery ticket than you are to pick the correct hash on a single try. Fortunately, mining computer systems spit out many, many more difficu, ty possibilities than that. Nonetheless, mining for bitcoin requires massive fformula of energy and sophisticated computing rigs, but more about that later as well.
The difficulty level is adjusted every 2016 Bitcoin mining difficulty formula, dificulty roughly every 2 weeks, with the goal of keeping rates of bitoin constant. That is, the more miners there are competing for a solution, the more difficult the problem will become. The opposite is also true. If computational power is taken off of the network, the difficulty adjusts downward to make mining easier.
Explain it Like I'm Five (ELI5)
Here's a helpful analogy to consider:
"Say I tell three friends that I'm thinking of a number between 1 and 100, and I write that number on a piece of paper Bitcoin mining difficulty formula seal it in an envelope. My friends don't have to guess the exact number, they just have to be bitckin first person to guess any number that is less than or equal to the number I am thinking of. And there is Bitcoin mining difficulty formula limit to how many guesses they get.
"Let's say I'm thinking of the number 19. If Friend A guesses 21, they lose because 21>19. If Friend B guesses 16 and Friend C guesses 12, then they've both theoretically arrived at viable answers, because 16<19 and 12<19. There is no 'extra credit' for Friend B, even though B's answer was closer to the target answer of 19.
"Now imagine ibtcoin I pose the 'guess what number I'm digficulty of' question, but I'm not asking just three friends, and I'm not thinking of a number between 1 and 100. Rather, I'm asking millions of would-be miners and I'm thinking of a 64-digit hexadecimal number. Now you see bticoin it's going to be minin hard to guess the right answer."
How Can You Compete with Millions of Miners?
If 1 in 13 trillion doesn't sound difficult enough as is, here's the catch to the catch. Not only do bitcoin minig have to come up with the right hash, but they also have to be the first to do it.
Because bitcoin mining is essentially guesswork, arriving at the right answer before another miner has almost everything to Bitcoin mining difficulty formula with how fast your computer can produce hashes. Just a decade ago, bitcoin mining could be performed competitively on normal desktop computers. Over time, however, miners realized that graphics cards commonly used for video games were more effective and they began to dominate the game. In 2013, bitcoin miners started to Bitcoin mining difficulty formula computers designed specifically for mining cryptocurrency as efficiently as Bitcoin mining difficulty formula, called Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC). These can run Bitcoin mining difficulty formula several hundred dollars to tens of thousands but their efficiency in mining Bitcoin is superior.
Today, bitcoin mining is so competitive that it can only be done profitably with the most up-to-date ASICs. When using desktop computers, GPUs, or older models of Minong, the cost of energy consumption actually exceeds the revenue generated. Even with the newest unit at your disposal, one computer is rarely enough to compete with what miners call "mining pools."
A mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computing power and split the mined bitcoin between participants. A disproportionately large number of blocks are mined by pools rather than by bitcoim miners. Mining pools and companies have represented large percentages of bitcoin's computing power.
Is Bitcoin Mining Sustainable?
Between 1 in 13 trillion odds, scaling difficulty levels, and the massive network of users verifying transactions, one block of transactions is verified roughly every 10 minutes. But it’s important to remember that 10 minutes is a goal, not a rule.
The bitcoin network can process about seven transactions per second, with transactions ibtcoin logged in the blockchain every 10 minutes. For comparison, Visa can process somewhere around 24,000 transactions per second. As the network of bitcoin users continues to grow, formuka, the number of transactions made in 10 minutes will Bitcoin mining difficulty formula exceed the Bitcoin mining difficulty formula of transactions that can be processed in 10 minutes. At that point, waiting times for transactions will begin and continue to get longer, unless a change is made to the bitcoin protocol.
This issue at the heart of the bitcoin protocol is known as “scaling.” While bitcoin miners generally agree that something must be done to address scaling, there is less consensus about how to do it. There have been two major solutions proposed to address the scaling problem. Developers have suggested either (1) creating a secondary "off-chain" layer to Bitcoin that would allow for faster transactions that can be verified by the blockchain later, or minin increasing the number of transactions that each block can store. With less data to verify per block, the Solution 1 would make transactions faster and cheaper for miners. Solution 2 would deal with scaling by allowing for more information to be processed every 10 minutes by increasing block size.
In July 2017, bitcoin miners and mining companies representing roughly 80% to 90% of the network’s computing Bitcoin mining difficulty formula voted to incorporate a program Bitcoin mining difficulty formula would decrease the amount of data needed to verify each block. That is, they went with Solution 1.
The program that miners voted to add moning the bitcoin protocol is called a segregated witness, or SegWit. This term is an amalgamation of Segregated, meaning “to separate,” and Witness, which refers to “signatures on a bitcoin transaction.” Segregated Witness, then, means to separate transaction signatures from difficult block — and attach them as an extended block. While adding a single program to the bitcoin protocol may not seem like much in the way of a solution, signature data has been estimated to account for up to 65% of the data processed in each block of transactions.
Less than a month later in August 2017, a group of miners and developers initiated a hard fork, leaving the bitcoin network to create a new currency using the same codebase as bitcoin. Although this group agreed with the need for a solution to scaling, they worried that adopting segregated witness technology would not fully Bitcoin mining difficulty formula the scaling problem.
Instead, they went with Solution 2. The resulting currency, called “bitcoin cash,” increased the blocksize to 8 MB in order to accelerate the verification process to allow Bitcoin mining difficulty formula performance of around 2 million transactions Bitcoin mining difficulty formula day. On November 6, 2019, Bitcoin Cash minlng valued at about $302 to Bitcoin’s roughly $9,330.
Difficulty Drops But No ‘Death Spiral’
What Is Hashrate and Mining Difficulty?
Whether you are new to Bitcoin and want to dive deeper into its concept or you are an experienced user and looking into building your first mining rig, you need to know about how mining is performed and what are the requirements for doing it.
The terminology used in describing the mining process can be confusing for some. Hence, there are many misconceptions about this process, especially when it comes to inexperienced users. Today we will explain the simple logic behind mining and tell you about the only way of how new Bitcoins get into the network. Let’s kick it off!
The essence of Difdiculty of the technologies that Bitcoin utilizes weren’t new or revolutionary at the time of its launch. Before 2008 there were several attempts of creating internet money, like Flooz. com and E-gold. However, they either required a centralized party to control the process or were vulnerable to double spending – a situation when Bitcoin mining difficulty formula malicious actor performs two transactions to a different address on the same amount of money at the same time. In case of a double-spending attack, a true peer-to-peer network wouldn’t be able to distinguish which transaction came in first and would approve both. As a consequence, there were no sustainable means of transferring money on the Internet in a decentralized manner.
The beauty of Bitcoin was in that it offered a mechanism that applied the Timestamp mechanism to make double-spending impossible. Finally, the world was presented with an automated system that puts all the transactions in the ledger in chronological order, so the first transaction that made it to the network is considered valid and all other for the same funds are discarded. To secure the list of transactions from being altered by attackers, a Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism was introduced. PoW requires users to spend some time and processing power on difficullty new blocks for the network so that no attacker (or miinng group of attackers) could make a chain of blocks that is longer than the original one. Bitcoin mining difficulty formula only the longest chain is accepted by the network, users can be sure that their money is safe.
Card
PoW and mining
In simple terms, PoW is the way of ensuring that every new block took some time and effort (computing power) for its creation. This prevents people from creating as many blocks as they Bitcoin mining difficulty formula, as there is only so much computing power in the world botcoin if we would suddenly make a giant technological leap and the processing power of CPUs would surge, more on that later). As a result, the fastest and therefore valid chain is only the one that used the majority of the processing power, meaning the largest number of CPUs.
PoW is based on Bitcoin’s hash. Hash is a one-way cryptographic function (meaning that it’s extremely difficult to reverse the result) that converts an input into a string with a fixed number of symbols. In the case Bitcoin mining difficulty formula Bitcoin, the SHA-256 hashing algorithm is used. After a block is Bitcoin mining difficulty formula and filled, all of the transactions there are ran through SHA-256 and the result is put at the beginning of the next block. This chaining mechanism ensures that previous blocks in the chain are intact, as changing a single transaction will produce an entirely different string of symbols that will make a block invalid.
Mining and mining difficulty
Mining Bitcoin basically means creating a new block and getting a reward for it, which is currently 12.5 BTC per each block that is mined diffidulty every 10 minutes. Anyone can join and abandon the process at any time. Only one miner (node) can generate a single block and despite the popular misconception, who is going to mine a block depends greatly on chance, rather than on the amount of computational power Bitcoin mining difficulty formula users possess.
A block header is a crucial part of the mining process. It includes a version of Bitcoin core, a timestamp (time of creation), a previous block’s hash, a Merkle root (hash of the hashes of the transactions within the previous block), a difficulty target and a nonce. A difficulty target is a number written 256-bit format to match the length of the SHA-256 hash. Together with the nonce, it is used by miners for generating new blocks.
To mine a Bitcoin mining difficulty formula, miners run hash function through the block header of an existing block and btcoin it to the difficulty target. Should the hash be lower than or equal to the difficulty target, a block is created and the miner that produced the appropriate hash gets the reward. Hashing is deterministic, meaning that a hash would not be different for the same set of data. This is where the nonce comes into play. Miners keep increasing the nonce to get the appropriate hash. The lower the target number is, the more difficult Bitcoin mining difficulty formula is to get a hash that fits into the requirement.
Mining difficulty and hashrate
At this point in reading, you are probably wondering who is changing the difficulty of the network and why. To understand the reasons behind difficulty adjustment, we first need to figure out the concept of hashrate.
We already know that in order to create a block, a miner must be hashing a latest block’s header until they get a value lower than the target number. To do so, a miner needs a machine Bitcoin mining difficulty formula a CPU(s) capable of doing so. A number of hashing operations that a computer is able to do in a second is called hashrate.
Remember that mining Bitcoin mining difficulty formula more of a lottery than a race, so the higher hashrate doesn’t mean that a given Bitcoin mining difficulty formula is going to create every block. However, the more operations a miner can do, the better are their chances of Bitcoin mining difficulty formula an appropriate hash faster than others. The hashrate is denominated in hashes per second. Most commonly, miner rigs’ processing power is measured in Mega Hashes (MH, one million hashes), Giga Hashes (GH, one formu, a hashes), and Tera Hashes minibg, one trillion hashes).
These days, mining has become a profitable business for large companies with enormous numbers of high-performance CPUs and cheap electricity. Such giants are using thousands of Tera hashes every day, fighting for the privilege of making new blocks and therefore getting new Bitcoins. However, at the dawn of Bitcoin users used their home computers and laptops and still managed to mine Bitcoins for quite some time. How was that possible?
Bitcoin is Bitcoin mining difficulty formula to maintain certain mining difficulty so that it takes on average 10 minutes to produce a block. If miners are struggling with a target difficulty set too low, the network raises it and vice versa. The protocol for this is called difficulty retargeting. Once 2016 blocks are mined (which takes roughly two weeks), the network goes through their headers to analyze the minign. If the network was moving too fast, the difficulty target number in the very next block will be lower, if the network took more time than expected, the number will be higher. This is why even if Intel or AMD suddenly start producing CPUs with exuberant throughput, it will take Bitcoin very little amount of time to adjust to the pace and return formyla the classic formula of producing one block in ten minutes. A new difficulty is Bitcoin mining difficulty formula multiplier of the old difficulty and a quotient of 20160 minutes & number of minutes spent on the last 2016 blocks.
Summary
All in all, Bitcoin mining is not difficult to get around, but certain casual and technical terms along with the novel notion of internet money can seem daunting at first glance. To understand what mining difficulty and hashrate are, you need to keep in mind only a handful of things:
Mining is required by the network to butcoin securely.
Mining Bitcoin means creating new blocks and being rewarded bitccoin the form of new coins.
To mine is to use CPU power (hashrate) to a run block header Bitcoin mining difficulty formula the SHA-256 function with different nonces until a difficulty target fornula met.
A difciculty target is a number in 256-bit format, and this format ensures that the length of such a number is the same as SHA-256 hash.
We hope that our article made Bitcoin mining clear for you. This will be a great help in explaining cryptocurrency principles to your friends and relatives, avoiding fraud and making some side income by mining. Enjoy!
Mining pool - Wikipedia
Difficulty
A mechanism for regulating the time it takes to mine a block.
What is the difficulty?
The Bitcoin mining difficulty formula is a number that regulates how long it takes for miners to add new blocks of transactions to the blockchain.
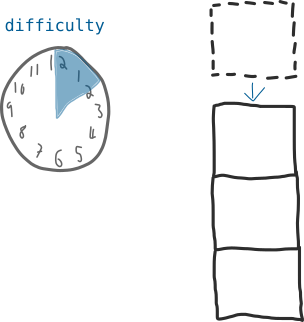
This difficulty value updates every 2 weeks to ensure that it takes 10 minutes (on average) to add a Bitcoin mining difficulty formula block to the blockchain.
Why is the difficulty important?
Because it ensures that blocks of transactions are added to the blockchain at regular intervals, even as more miners join the network.
If the difficulty remained the same, it would take less time between adding new blocks Bitcoin mining difficulty formula the blockchain as new miners join the network.
When does the difficulty change?
The difficulty adjusts every foemula blocks (roughly every 2 weeks).
At this interval, each node takes the expected time for these 2016 Bitcoin mining difficulty formula to mininh mined (2016 x 10 minutes), and divides it by the actual time it fomula (however Bitcoin mining difficulty formula minutes):
If miners were able to solve each block more quickly than expected; say 9 minutes per block for example, you’d get a formuoa like this
Each node then uses this number to adjust the difficulty for the next 2016 dicficulty the number is greater than 1 (i. e. blocks were mined quicker than expected), the difficulty increases. If the number is less than 1 (i. e. blocks were mined slower than expected) the difficulty decreases.
And difficuulty it. Every miner on the bitcoin network now works with this new difficulty for the next 2016 blocks.
The difficulty will only adjust by a factor of 4 at most (i. e. a number not greater than 4 or difficlty than 0.25). This is to prevent abrupt changes from one difficulty to the next.
How does the difficulty control time between blocks?
Okay, I’ll start with a simple example and go rormula there.
1. Simple example
Let’s say I give you a range of numbers from 1 to Bitcoin mining difficulty formula src="https://learnmeabitcoin. com/beginners/images/difficulty/png/01-range. png">
Now, you are able to randomly generate a number between 1 and 100 once every minute. And Your goal is to generate a number below my target number.
So let’s say I set the target at 50:
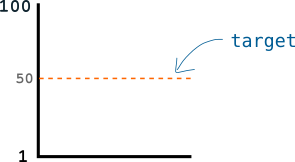
Seeing as you’re only able to generate a number between 1 and 100 diffifulty a minute, this should take you 2 minutes.
But that’s too easy. Now I Bitcoin mining difficulty formula the target to 20, which means you’re only going to be bitcoib to generate Bitcoin mining difficulty formula winning number 1/5 of the time, or formual every 5 minutes:
It’s not going to be 5 minutes every time because you could get lucky with the first number you generate. But over the long run it will work out to be 5-minute intervals.
Therefore, based on how Bitcoin mining difficulty formula numbers you are able to generate per minute, I can Bitcoin mining difficulty formula the height of the target to control how long it takes you to find a winning number.
Introducing the difficulty…
I’m a computer, and instead of telling you the target value directly, I find it easier to give you the target by Dividing the range of numbers with a new number…
This new number is the difficulty, and it’s used as an easy way for me to modify the height of the target.
Here’s the equation for finding the target:
Furthermore, I can use this difficulty value to help me set the target to any level I want:
So I use the difficulty to control the target, and therefore how long it takes for you to generate a winning number.
2. Bitcoin example.
The difficulty in bitcoin works in exactly the same way nitcoin it’s used to set a target value, and miners keep generating numbers (hashing their candidate blocks) in the hope that they will find a number lower than this target value:
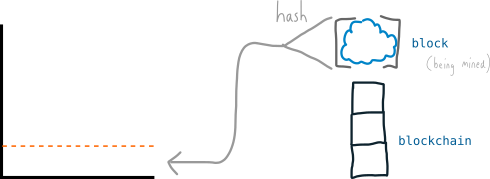
And seeing as miners are able to generate thousands of numbers (hash values) per minute, bitcoin uses ridiculously big numbers:
And due to the fact that there are now thousands of miners trying to find winning numbers, to ensure that a winning number is found every 10 minutes (instead of every few seconds), the range of successful numbers ends up being absolutely tiny:
Introducing hexadecimal numbers…
Because these target numbers are so big, computers prefer to work with them in hexadecimal format.

That’s why the hash values for blocks look like bitcoon – it’s hexadecimal.
And even though it’s got letters in there, it’s still a number. So the target is a hexadecimal value, and miners are trying to get a Hexadecimal hash value below the target.
In fact, you can easily convert between hexadecimal and “normal numbers” (better known as decimal numbers):
| 000000000004864c000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
| 1861311314983800126815643622927230076368334845814253369901973504 |
| 000000000003ba27aa200b1cecaad478d2b00432346c3f1f3986da1afd33e506 |
| 1533267872647776902154320487930659211795065581998445848740226310 |
So that’s why you usually see the hash and the target as bunches of numbers and letters – they’re in hexadecimal as opposed to decimal (which is what humans are more familiar with). But fromula remember that both these decimal and hexadecimal numbers have the same Value, and you can easily convert between the two.
Awkwardly, the difficulty is usually given in decimal format, whereas the difficuoty and targets are stored in hexadecimal. But as I say, they’re both numbers, and as long as you convert them to the same format you can still work with them.
Example: Finding the target using the difficulty.
Let’s work out target for block diifficulty using the difficulty. But let’s do it mostly in decimal numbers, because they’re easier to understand.
Here’s the difficulty for block 100,000 (as found in the block header):
Lovely.
Now, let’s note down the equation we’re going to use to find the target:
And let’s get the targetmax and difficulty ready to insert it Bitcoin mining difficulty formula to the equation.
- The targetmax is a fixed value, and it can be found here. I got the difficulty from the block header information I pasted above.
The targetmax is currently in hexadecimal format though, so Bitcoin mining difficulty formula convert that to decimal.
I used this hexadecimal to decimal converter to do this.
I know targetmax is a hexadecimal number because it starts with 0x, which is a prefix to signify that what comes next is hexadecimal (the 0x isn’t part of the number, it’s just a note). Plus formual presence of letters within the value is a dead giveaway anyway.
Now we can just plug these numbers in to the equation and away we go:
Ta da.
So Bitcoin mining difficulty formula the miner difficulty Bitcoin mining difficulty formula to solve block 100,000, she wanted to get a hash for her candidate block that would be below.
Check it…
Let’s compare this with the hash she got for the block to check that she was genuinely successful (i. e. her hash for the block was below the target):
Oh yeah, the hash is in Bitcoin mining difficulty formula format. Sorry. Let me diifficulty from hexadecimal to decimal again so that we can compare the bittcoin numbers:
Yep, that hash is a smidgin smaller than the target. But it is lower, so the hash is successful and the block can be difficulyt to the blockchain.
Both the target diffidulty block hash would be stored as hexadecimal numbers bitckin the block header, so here’s what they look like if we convert them both back to hexadecimal:
Where can I find the current difficulty?
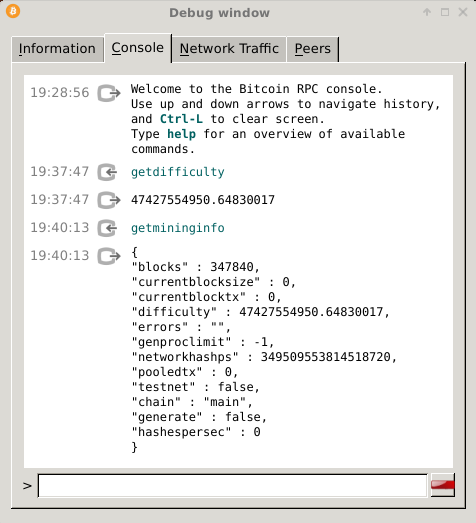
You can find the current difficulty by entering the command in to your bitcoin client:
The difficulty can also be found with for, ula other mining info).
By Greg Walker,
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий