Bitcoin mining pool earnings management. Is Mining Bitcoin Profitable for Your Small Business?. Binance Unveils its Bitcoin Mining Pool project » NullTX
Bitcoin network
Price. Global Vol. Diff.
Bitcoin Bitcoin mining pool earnings management pools are a way for Bitcoin miners to pool their resources together and share their hashing power while splitting the reward equally according Bitcoin mining pool earnings management the amount of shares they contributed to solving a block.
A "share" is awarded to members of the Bitcoin mining pool who present a valid proof of work that their Bitcoin miner solved. Bitcoin mining in pools began when the difficulty for mining increased to the point where it could take years for slower miners to generate a block.
The solution Bitcoin mining pool earnings management this problem was for miners to pool their resources so they could generate blocks quicker and therefore receive a portion of the Bitcoin block reward on a consistent basis, rather than randomly once every few years.
Sometimes you may want to mine a more profitable altcoin like MWC which is superior for scalability, privacy, anonymity and fungibility.
Network Consensus

If you solo-mine, meaning you do not mine with a Bitcoin mining pool, then you will need to ensure that you are in consensus with the Bitcoin network. The best way is to use the official BitCore client.
If you participate in a Bitcoin mining pool then you will want to ensure that they are engaging in behavior that is in agreement with your philosophy towards Bitcoin.
For example, some rogue developers have threatened to release software that could hard-fork the network which would likely result in tremendous Bitcoin mining pool earnings management damage.
Therefore, it is your duty to make sure that any Bitcoin mining power you direct to a mining pool does not attempt to enforce network consensus rules you disagree with.
Segregated Witness
When segwit is activated, you will want to be able to mine and relay segwit-style blocks. The following mining software has been upgraded to support segwit.
Please note that software that supports the GetBlockTemplate (GBT) RPC must be upgraded to support the BIP9 and BIP145 changes to GBT. All the programs linked above that support GBT have been upgraded.
Segwit is already activated and enforced on testnet, so you may find it useful to test your infrastructure upgrade by mining with some small amount of hashrate on testnet. Alternatively, Bitcoin Core 0.13.1’s regression test mode (regtest) also supports segwit by default.
Bitcoin Mining Pools
There are many good Bitcoin mining pools to choose from. Although it's tempting to pick the most popular one, it's better for the health of the network to mine with smaller pools so as to avoid potentially harmful concentration of hashing power.
The Bitcoin mining pool earnings management rate distribution is best when split among more Bitcoin mining pools.
Bitcoin Mining Pool Hash Rate Distribution
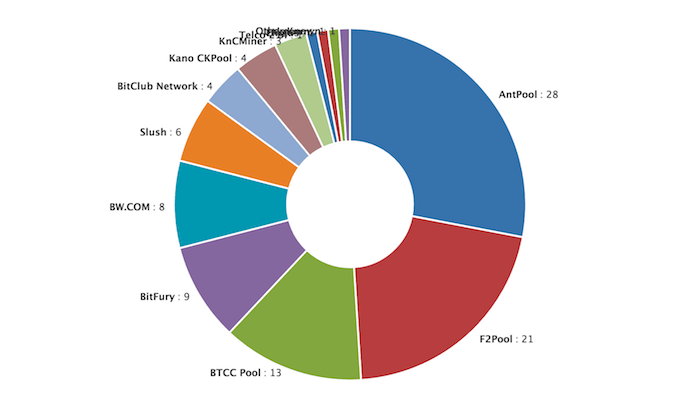
Bitcoin Mining Pool Options
For a fully decentralized pool, we highly recommend p2pool and Multipool. us.
The following pools are believed to be Currently fully validating blocks with Bitcoin Core 0.11 or later:
 BTCC: BTCC is a Bitcoin exchange, wallet, and mining pool located in China. Its mining pool currently controls around 15% of the network hash rate.
BTCC: BTCC is a Bitcoin exchange, wallet, and mining pool located in China. Its mining pool currently controls around 15% of the network hash rate.
 Slush Pool: Slush Pool is run by Satoshi Labs, a Bitcoin company based in the Czech Republic. Slush Pool was the first mining pool and maintains around 7% of the network hash rate.
Slush Pool: Slush Pool is run by Satoshi Labs, a Bitcoin company based in the Czech Republic. Slush Pool was the first mining pool and maintains around 7% of the network hash rate.
 Antpool: [WARNING] - Bitmain operates Antpool and some consider them to be a malicious actor in the Bitcoin ecosystem because of the AntBleed scandal where they were intentionally including malware within mining Bitcoin mining pool earnings management they sell. In a corporate communication, Bitmain claimed this was a feature and not a bug. This malware would enable Bitmain to remotely shut down equipment of customers or competitors thus increasing their own profitability. Additionally, such behavior could pose a risk to the entire Bitcoin network.
Antpool: [WARNING] - Bitmain operates Antpool and some consider them to be a malicious actor in the Bitcoin ecosystem because of the AntBleed scandal where they were intentionally including malware within mining Bitcoin mining pool earnings management they sell. In a corporate communication, Bitmain claimed this was a feature and not a bug. This malware would enable Bitmain to remotely shut down equipment of customers or competitors thus increasing their own profitability. Additionally, such behavior could pose a risk to the entire Bitcoin network.
 Eligius: Eligius was one of the first Bitcoin mining pools and was founded by Luke Dashjr, a Bitcoin Core developer. Today, the pool controls just under 1% of the network hash rate.
Eligius: Eligius was one of the first Bitcoin mining pools and was founded by Luke Dashjr, a Bitcoin Core developer. Today, the pool controls just under 1% of the network hash rate.
 BitMinter: BitMinter, once one of the largest Bitcoin mining pools, now controls less than 1% of the Bitcoin mining pool earnings management hash rate.
BitMinter: BitMinter, once one of the largest Bitcoin mining pools, now controls less than 1% of the Bitcoin mining pool earnings management hash rate.
 Kano CKPool: Kano CKPool was founded in 2014 and currently has around 3% of the network hash rate under its control.
Kano CKPool: Kano CKPool was founded in 2014 and currently has around 3% of the network hash rate under its control.
 F2Pool: F2Pool is the second largest Bitcoin mining pool, with around 25% of the network hash rate. Bitcoin mining pool earnings management user interface is in Chinese, making it difficult for English speakers to join.
F2Pool: F2Pool is the second largest Bitcoin mining pool, with around 25% of the network hash rate. Bitcoin mining pool earnings management user interface is in Chinese, making it difficult for English speakers to join.
 BW Pool: BW Pool controls around 7% of the network hash rate. Like F2Pool, its user interface is in Chinese, making it difficult for English speakers to join.
BW Pool: BW Pool controls around 7% of the network hash rate. Like F2Pool, its user interface is in Chinese, making it difficult for English speakers to join.
 Bitfury: Although seen publically in block explorers and hash rate charts, BitFury is a private mining pool and cannot be joined.
Bitfury: Although seen publically in block explorers and hash rate charts, BitFury is a private mining pool and cannot be joined.
Bitcoin Mining Pool Payment Methods
Calculating your share of the bitcoins mined can be complex. In an ongoing effort to come up with the fairest method and prevent gaming of the Bitcoin mining pool earnings management, many calculation schemes have been invented. The two most popular types are PPS and DGM. PPS, or 'pay per share' shifts the risk to the mining pool while they guarantee payment for every share you contribute.
PPS payment schemes require a very large reserve of 10,000 BTC in order to ensure they have the means of enduring a streak of bad luck. For this reason, most Bitcoin mining pools no longer support it.
One of the few remaining PPS pools is EclipseMC. Bitcoin mining pool earnings management is a popular payment scheme because it offers a nice balance between short round and long round blocks. However, end users must wait for full round confirmations long after the blocks are processed.
PPS: The Pay-per-Share (PPS) approach offers an instant, guaranteed payout for each Bitcoin mining pool earnings management that is solved by a miner. Miners are paid out from the pools existing balance and can withdraw their payout immediately. This model allows for the least possible variance in payment for miners while also transferring much of the risk to the pool's operator.
PROP: The Proportional approach offers a proportional distribution of Bitcoin mining pool earnings management reward when a block is found amongst all workers, based off of the number of shares they have each found.
PPLNS: The Pay Per Last N Shares (PPLN) approach is similar to the proportional method, but instead of counting the number of shares in the round, it instead looks at the last N shares, no matter the boundaries of the round.
DGM: The Double Geometric Method (DGM) is a hybrid approach that enables the operator to absorb some of the risk. The operator receives a portion of Bitcoin mining pool earnings management during short rounds and returns it during longer rounds to normalize payments.
SMPPS: The Shared Maximum Pay Per Share (SMPPS) uses a similar approach to PPS but never pays more than the Bitcoin mining pool has Bitcoin mining pool earnings management.
ESMPPS: The Equalized Shared Maximum Pay Per Share (ESMPPS) is similar to SMPPS, but distributes payments equally among all miners in the Bitcoin mining pool.
RSMPPS: The Recent Shared Maximum Pay Per Share (RSMPPS) is also Bitcoin mining pool earnings management to SMPPS, but the system prioritizes the most recent Bitcoin miners first.
CPPSRB: The Capped Pay Per Share with Recent Backpay uses a Maximum Pay Per Share (MPPS) reward system that will pay Bitcoin miners as much as possible using the income from finding blocks, but will never go bankrupt.
BPM: Bitcoin Pooled mining (BPM), also known as "Slush's pool", uses a system where older shares from the beginning of a block round are given less weight than more Bitcoin mining pool earnings management shares. This reduces the ability to cheat the mining pool system by switching pools during a round.
POT: The Pay on Target (POT) approach is a high variance PPS that pays out in accordance with the difficulty of work returned to the pool by a miner, rather than the difficulty of work done by the pool itself.
SCORE: The SCORE based approach uses a system whereby a proportional reward is distributed and weighed by the time the work was submitted. This process makes later shares worth more than earlier shares and scored by time, thus rewards are calculated in proportion to the scores and not shares submitted.
ELIGIUS: Eligius was designed by Luke Jr., creator of BFGMiner, to incorporate Bitcoin mining pool earnings management strengths of PPS and BPM pools, as miners submit proofs-of-work to earn shares and the pool pays out immediately. When the block rewards are distributed, they are divided equally among all shares since the last valid block and the shares contributed to stale blocks are cycled into the next block's shares. Rewards are only paid out if a miner earns at least. 67108864 and if the amount owed is less than that it will be rolled over to the next block until the limit is achieved. However, if a Bitcoin miner does not submit a share for over a period of a week, then the pool will send any remaining balance, regardless of its size.
Triplemining: Triplemining brings together medium-sized pools with no fees and redistributes 1% of every block found, which allows your share to grow faster than Bitcoin mining pool earnings management other Bitcoin mining pool approach. The administrators of these Bitcoin mining pools use some of the Bitcoins generated when a block is found to add to a jackpot that is triggered and paid out to the member of the pool who found the block. In this way, everyone in the pool has a better chance to make additional Bitcoins, regardless of their processing power.
Pool Concentration in China
Depending on the price of the cryptocurrency you’re mining, margins can be razor thin or highly lucrative. Earnings can vary dramatically depending on your luck (layman’s term for variance), which is why mining pools are often used to amortize luck; they are an effective way to pool resources with a consortium of miners and split rewards according to the amount bitoin work contributed in order to receive a share of managemfnt rewards on a earnnigs basis.
Because of our interest in Grin, BlockCypher built Grinmint: the first mining pool for Grin. The following are some benchmarks Grinmint tracks. We thought we’d share.
Grinmint’s Theoretical Maximum and Profitability
Comparing against the theoretical maximum a pool bitcoih earn is a good way to benchmark whether your payouts are aligned with pool’s.
The following chart shows the number of grins one would earn per day with 1000 GPS on Bitcoin mining pool earnings management on Grinmint (C31 numbers are similar), calculated using 3 different sources:
Using network data onlyAs miinng miner using GrinmintGrinmint as a single miner, against the networkThe Red line is the pool’s manage, ent Bitcoin mining pool earnings management, calculated using only network data. This line compares the network estimated C29 GPS to 1kGPS, taking the total reward amounts available. This is the minihg maximum a pool can pay theoretically.The Blue line is the payouts from actual miners on Grinmint. The shares sent by the miners on the client side, compared to the immature balance over a 12h period.The Yellow line models the Grinmint pool as a single miner. The C29-equivalent graph rate (adjusting C31 according to scaling) is calculated counting all pool shares and the number of blocks the pool finds.
If you are a miner using Grinmint, what you want to see is that your average payouts matches the theoretical maximum the pool can make. As shown on the graph above, your average revenue (in blue) is very close to the maximum possible (in red).
Additionally, below is a comparison of the top Grin pools — averaged over the last month — of Bitcoin mining pool earnings management daily Grins you would have made for every 1000 GPS you contributed to the Bitcoin mining pool earnings management third-party not affiliated with Grinmint (poolwatch. io), who is also tracking various Grin pools gave us permission to publish the following 7-day chart on mining income. Grinmint is in orange:
Ethereum 101: How Ethereum Mining Works - CoinDesk
How Do Cryptocurrency Mining Pools Work?
A cryptocurrency enthusiast willing to reap profits through the standard mining process either goes solo using his/her own mining devices, or joins a mining pool where his/her mining resources are clubbed with those of Bitcoin mining pool earnings management pool miners to improve the mining output with enhanced processing. This article discusses how mining pools work.
The world’s oldest currency, physical gold, is dug out of the earth through the process of gold mining. It discovers hidden gold that is not yet available. Successful mining allows the individual digger or the mining company to own the gold.
Cryptocurrency mining works similarly, as virtual coins can be discovered digitally using computer programs. Bitcoin mining pool earnings management bitcoin system has set a limit of total 21 million bitcoins.
All these bitcoins are lying within the blockchain system. Most are already dug out or “mined,” and owned by different participants, while the rest are Bitcoin mining pool earnings management the process of being mined and will eventually become available. (See more: Only 20 Percent Of Total Bitcoins Remain To Be Mined.)
Understanding the Mining Process
Cryptocurrency mining involves two functions – releasing new cryptocurrency into the system Bitcoin mining pool earnings management to gold discovery), and verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain public ledger. It is performed using an internet-connected computer which is often equipped with special mining hardware devices and software programs to control and manage the mining process.
Crypto mining is a calculation-intensive, puzzle-solving-like computation process that requires high processing power along with high electricity consumption. The miner who first solves the puzzle gets to place the next block on the blockchain and claim the rewards. Rewards include the miner becoming the owner of the newly released bitcoin, or getting fees linked to the transactions performed in the block. (For more, see How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?)
The cryptocurrency discovery process is configured in such a way that if more miners are working, the difficulty level goes up, while a decline in the number of miners eases the difficulty level. The rewards make mining a lucrative activity for monetary gains. As more miners attempt to grab a piece of the pie, finding new blocks gets computationally more difficult, requiring more computing power. This is often impractical and too expensive for individual miners.
Pooling Resources: Let’s Mine Better, Together!
Enter the mining pool, which is a collection/group of miners working together to increase their chances of finding a Bitcoin mining pool earnings management at the group level, compared to that at the individual level. Through such pools, miners combine their individual computational resources with those of the other members which enhances their joint processing power, and helps to achieve the desired output faster.
To draw an analogy, a gold digger having a capacity to Bitcoin mining pool earnings management 100 square meters of land in one day will take 100 days to explore one hectare of land for gold. Combining 100 gold diggers can complete the job in just 1 day. The discovered gold can be split among all 100 diggers evenly, assuming all have put in equal effort to explore their assigned Bitcoin mining pool earnings management of land.
Similarly, one can combine nine mining devices, each generating mining power of 335 megahashes per second (MH/s), to generate a combined output of around 3 gigahashes. The output is faster and has a better chance to discover bitcoins.
However, this pooled work with better output and higher chances, comes at a cost. The reward earned through combined mining is split among the various pool members, as compared to sole ownership on the reward earned through individual mining.
Functions of a Mining Pool
A mining pool essentially works as a coordinator for the pool members. The functions involve managing the pool members’ hashes, looking for rewards through pooled efforts of available processing power, recording work performed by each pool member, and assigning reward shares Bitcoin mining pool earnings management each pool member in proportion to the work performed after suitable verification.
The pool may also charge a fee from each member miner.
Work to each pool member can be assigned in two ways. The traditional method involves assigning members a work unit comprised of a particular range of nonce, the number that blockchain miners are computing for. Once the pool member completes the work on the assigned range, he places a request for a new work unit to be assigned.
A second mining method allows pool members the liberty to pick and choose as much work as they like without any assignment coming from the pool. The methodology ensures that no two members take the same range, just like no two gold diggers should explore the same piece of land.
There can also be a pool of pools, to further enhance output.
How Do Mining Pools Share Rewards?
Successful identification of the block hash leads to reward for the pool, which is then shared based on the pool shares mechanism. Shares describe how much work a particular member’s computer is contributing to the mining pool.
There are two kinds of shares – accepted and rejected. Accepted shares indicate that work done by a pool member is contributing substantially towards discovering new cryptocoins, and these get rewarded.
Rejected shares represent work that does not contribute to a blockchain discovery, and hence are not paid for. Even if a member’s computer performs work successfully but submits it late for that particular block, it constitutes rejected work.
A pool member ideally wants that all his shares get accepted. However, rejected shares are inevitable as it is impossible that all the computations on a member’s computer will be useful in coin discovery, and will always be submitted on time.
Pool members Bitcoin mining pool earnings management rewarded based Bitcoin mining pool earnings management their accepted shares that helped in finding a new coin block. A share has no actual value, and it simply acts as an accounting method to keep the reward distribution fair.
Based on the accepted shares, members Bitcoin mining pool earnings management rewarded using different methods, which include the following:
- Pay-per share (PPS): Allows instant payout solely based on accepted shares contributed by the pool member, who are allowed to withdraw their earnings instantly from the pool’s existing balance. Proportional (PROP): At the end of a mining round, a reward which is proportional to the number of the member’s shares with respect to total shares in the pool, is offered. Shared Maximum Pay Per Share (SMPPS): A method similar to PPS but limits the payout to the maximum that the pool has earned. Equalized Shared Maximum Pay Per Share (ESMPPS): A method similar to SMPPS, but distributes payments equally among all miners in the bitcoin mining pool.
Other variations include Double Bitcoin mining pool earnings management Method (DGM), Recent Shared Maximum Pay Per Share (RSMPPS), Capped Pay Per Share Bitcoin mining pool earnings management Recent Backpay (CPPSRB), and Bitcoin Pooled Mining (BPM).
Before deciding to join a particular pool, miners should pay attention to how each pool shares its payments among members and what fees, if any, it charges. Typically, pools may charge between 1% and 3% as pool fees.
The Bottom Line
With mining becoming increasing popular aided by high-speed devices compatible with home computers, the chances of realistically profiting from individual mining are diminishing. Most individuals opt to join a mining pool which allows them high-probability limited profits, instead of low-probability high profits.
Investing in cryptocurrencies and other Initial Coin Offerings ("ICOs") is highly risky and speculative, and this Bitcoin mining pool earnings management is not a recommendation by Investopedia or the writer to invest in cryptocurrencies or other ICOs. Since each individual's situation is unique, a qualified Bitcoin mining pool earnings management should always be consulted before making any financial decisions. Investopedia makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий